Hyundai Elantra CN7: ESC (Electronic Stability Control) System
Hyundai Elantra CN7: ESC (Electronic Stability Control) System
Description and operation
| Description of ESP |
ESP recognizes critical driving conditions, such as panic reactions in dangerous situations, and stabilizes the vehicle by wheel-individual braking and engine control intervention.
ESP adds a further function known as Active Yaw Control (AYC) to the ABS, TCS, EBD and ESP functions. Whereas the ABS/TCS function controls wheel slip during braking and acceleration and, thus, mainly intervenes in the longitudinal dynamics of the vehicle, active yaw control stabilizes the vehicle about its vertical axis.
This is achieved by wheel individual brake intervention and adaptation of the momentary engine torque with no need for any action to be taken by the driver.
ESP essentially consists of three assemblies : the sensors, the electronic control unit and the actuators.
The stability control feature works under all driving and operating conditions. Under certain driving conditions, the ABS/TCS function can be activated simultaneously with the ESP function in response to a command by the driver.
In the event of a failure of the stability control function, the basic safety function, ABS, is still maintained.
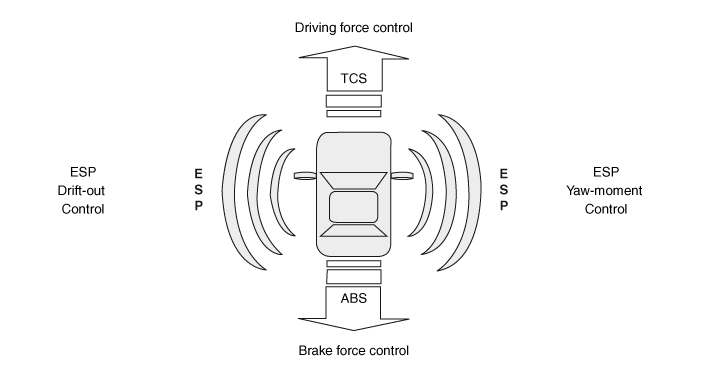
Description of ESP Control
ESP system includes ABS/EBD, TCS and AYC function.
ABS/EBD function : The ECU changes the active sensor signal (current shift) coming from the four wheel sensors to the square wave. By using the input of above signals, the ECU calculates the vehicle speed and the acceleration & deceleration of the four wheels. And, the ECU judges whether the ABS/EBD should be actuated or not.
TCS function prevents the wheel slip of drive direction by adding the brake pressure and engine torque reduction via CAN communication. TCS function uses the wheel speed sensor signal to determine the wheel slip as far as ABS function.
AYC function prevents unstable maneuver of the vehicle. To determine the vehicle maneuver, AYC function uses the maneuver sensor signals(Yaw Rate Sensor, Lateral Acceleration Sensor, Steering Wheel Angle Sensor).
If vehicle maneuver is unstable (Over Steer or Under Steer), AYC function applies the brake pressure on certain wheel, and send engine torque reduction signal by CAN.
After the key-on, the ECU continually diagnoses the system failure. (self-diagnosis)If the system failure is detected, the ECU informs driver of the system failure through the BRAKE/ABS/ESP warning lamp. (fail-safe warning)
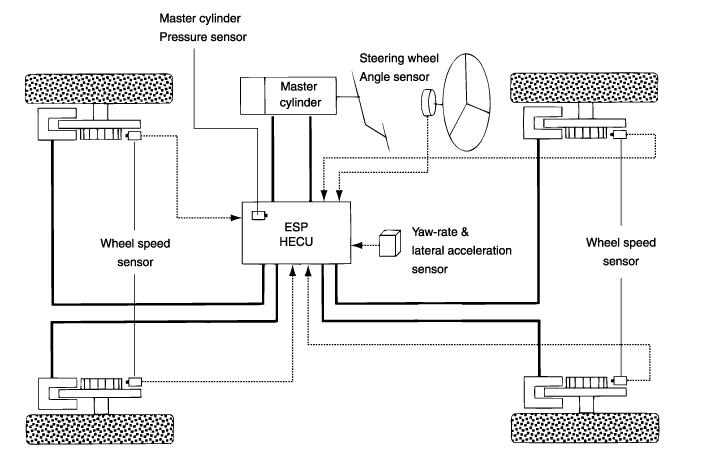
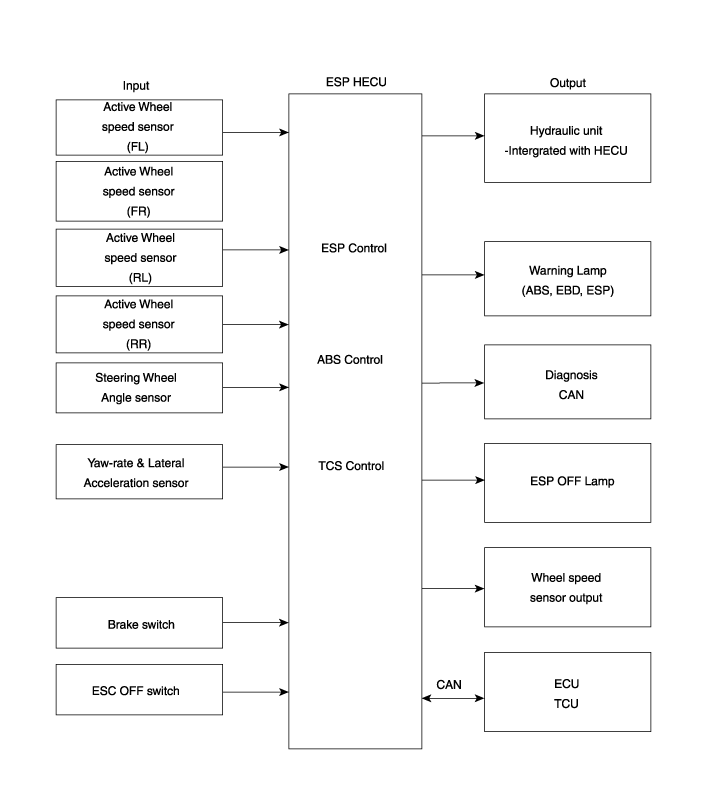
Input and Output Diagram
| ESP Operation Mode |
| 1. | STEP 1 The ESP analyzes the intention of the driver.
|
| 2. | STEP 2 It analyzes the movement of the ESP vehicle.
|
| 3. | STEP 3 The HECU calculates the required strategy, then actuates the appropriate valves and sents torque control requests via CAN to maintain vehicle stability.
|
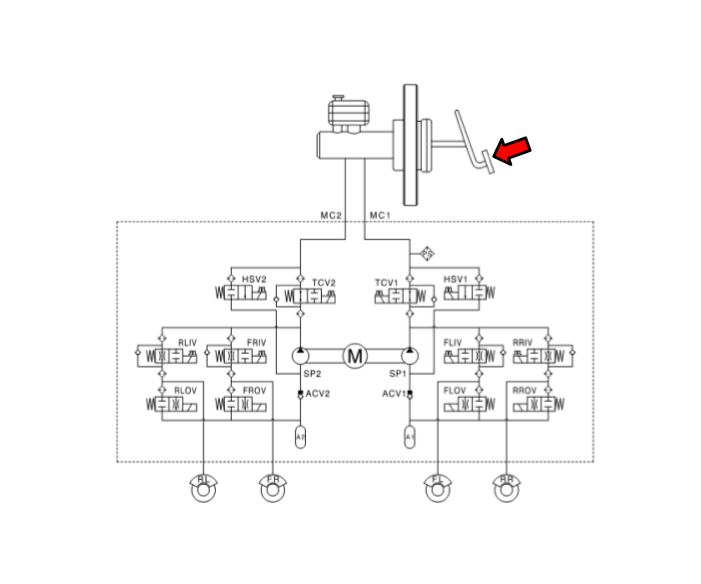
| ESP Hydraulic System Diagram |
| 1. | ESP Non-operation : Normal braking.
|
| 2. | ESP operation
Warning Lamp Control
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
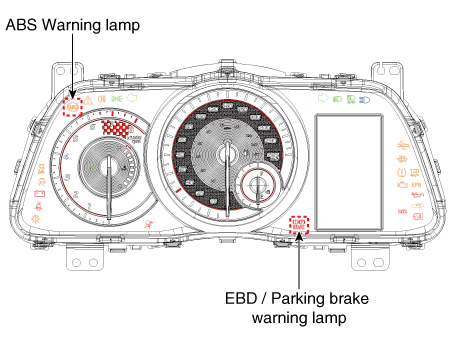
ABS Warning Lamp module
The active ABS warning lamp module indicates the self-test and failure status of the ABS. The ABS warning lamp shall be on :
| – | During the initialization phase after IGN ON. (continuously 3 seconds). |
| – | In the event of inhibition of ABS functions by failure. |
| – | During diagnostic mode. |
| – | When the ECU Connector is seperated from ECU. |
| – | Cluster lamp is ON when communication is impossible with CAN module. |
EBD/Parking Brake Warning Lamp Module
The active EBD warning lamp module indicates the self-test and failure status of the EBD. However, in case the Parking Brake Switch is turned on, the EBD warning lamp is always turned on regardless of EBD functions. The EBD warning lamp shallbe on :
| – | During the initialization phase after IGN ON. (continuously 3 seconds). |
| – | When the Parking Brake Switch is ON or brake fluid level is low. |
| – | When the EBD function is out of order . |
| – | During diagnostic mode. |
| – | When the ECU Connector is seperated from ECU. |
| – | Cluster lamp is ON when communication is impossible with CAN module. |
ESP Function / Warning Lamp (ESP System)
The ESP function/warning lamp indicates the self-test and failure status of the ESP.
The ESP function/warning lamp is turned on under the following conditions :
| – | During the initialization phase after IGN ON. (continuously 3 seconds). |
| – | When the ESP function is inhibited by system failure. |
| – | When the ESP control is operating. (Blinking - 2Hz) |
| – | During diagnostic mode.(Except standard mode) |
| – | Cluster lamp is ON when communication is impossible with CAN module. |
ESP OFF Lamp (ESP System)
The ESP Off lamp indicates the self-test and operating status of the ESP.
The ESP Off lamp operates under the following conditions :
| – | During the initialization mode after IGN ON. (continuously 3 seconds). |
| – | ESP Off lamp is On when driver input the ESP Off switch. |
ESP ON / OFF Switch (ESP System)
The ESP On/Off Switch shall be used to toggle the ESP function between On/Off states based upon driver input.
The On/Off switch shall be a normally open, momentary contact switch.Closed contacts switch the circuit to ignition.
Initial status of the ESP function is on and switch toggle the state.
Components and components location
| Components |
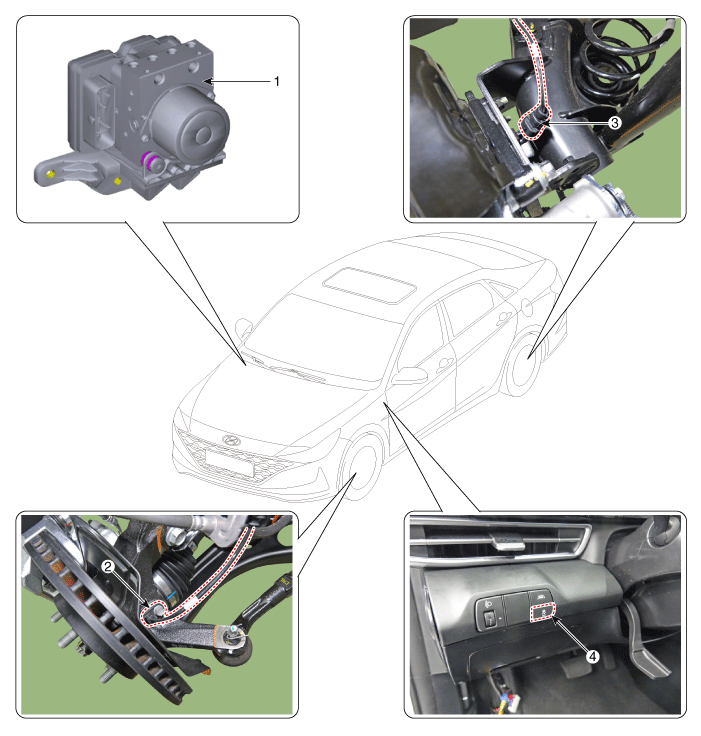
| 1. ESC control module (HECU) 2. Front wheel speed sensor | 3. Rear wheel speed sensor 4. ESC OFF switch |
Troubleshooting
| Failure Diagnosis |
| 1. | In principle, ESP and TCS controls are prohibited in case of ABS failure. |
| 2. | When ESP or TCS fails, only the failed system control is prohibited. |
| 3. | However, when the solenoid valve relay should be turned off in case of ESP failure, refer to the ABS fail-safe. |
| 4. | Information on ABS fail-safe is identical to the fail-safe in systems where ESP is not installed. |
Memory of Fail Code
| 1. | It keeps the code as far as the backup lamp power is connected. (O) |
| 2. | It keeps the code as far as the HCU power is on. (X) |
Failure Checkup
| 1. | Initial checkup is performed immediately after the HECU power on. |
| 2. | Valve relay checkup is performed immediately after the IG2 ON. |
| 3. | It executes the checkup all the time while the IG2 power is on. |
Countermeasures in Fail
| 1. | Turn the system down and perform the following actions and wait for HECU power OFF. |
| 2. | Turn the valve relay off. |
| 3. | Stop the control during the operation and do not execute any until the normal condition recovers. |
Warning Lamp ON
| 1. | ESP warning lamp turn on for 3sec after IGN ON. |
| 2. | ESP function lamp blinks when ESP Act. |
| 3. | If ESP fail occured, ESP warning turns ON. |
| 4. | ESP OFF lamp turn on in case of
|
Standard Flow of Diagnostic Troubleshooting
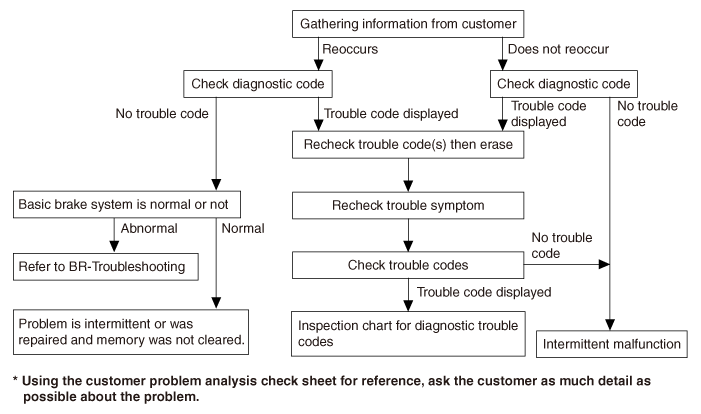
Notes With Regard to Diagnosis
The phenomena listed in the following table are not abnormal.
| Condition | Explanation | ||||||
| System check sound | When starting the engine, a thudding sound can sometimes be heard coming from inside the engine compartment. This is because the system operation check is being performed. | ||||||
| ABS operation sound |
| ||||||
| ABS operation (Long braking distance) | For road surfaces such as snow-covered and gravel roads, the braking distance for vehicles with ABS can sometimes be longer than that for other vehicles. Accordingly, advise the customer to drive safely on such roads by lowering the vehicle speed. |
Inspection method
With the IGN OFF, set the IGN to ON position : If the ABS/Brake Warning Light illuminates and distinguishes after 3 seconds, the warning lamp and ABS system are all normal.
| 1. | If the Warning Light does not illuminate when IGN is set to ON position
The Warning Light is normal and judged to be failure of the VDC system. Inspect the VDC system using GDS. |
| 2. | If the Warning Light does not distinguish after its illumination when IGN is set to ON position.
|
| 3. | Even if the Warning Light and VDC system are all normal, erase all the memorized fault codes using GDS (if there is no memorized fault code, record the fault code).
|
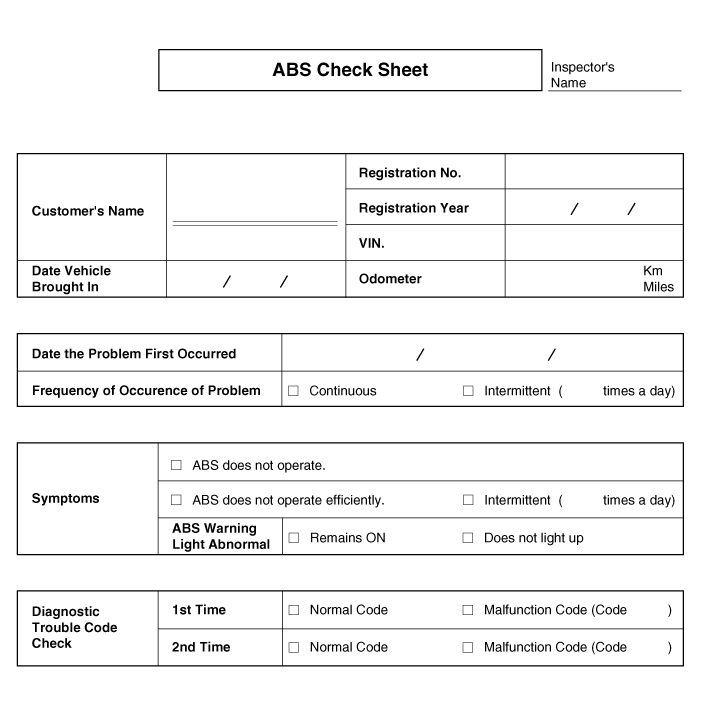
ABS Check Sheet
Problem Symptoms Table
| Symptom | Suspect Area | ||||||||
| ABS does not operate. | Only when 1 - 4 are all normal and the problem is still occurring, replace the HECU.
| ||||||||
| ABS does not operate intermittently. | Only when 1 - 4 are all normal and the problem is still occurring, replace the ABS actuator assembly.
| ||||||||
| Communication with GDS is not possible. (Communication with any system is not possible) |
| ||||||||
| Communication with GDS is not possible. (Communication with ABS only is not possible) |
| ||||||||
| When ignition key is turned ON (engine OFF), the ABS warning lamp does not light up. |
| ||||||||
| Even after the engine is started, the ABS warning lamp remains ON. |
|
|

Detecting condition
| Trouble Symptoms | Possible Cause | ||||||||
| Brake operation varies depending on driving conditions and road surface conditions, so diagnosis can be difficult. However if a normal DTC is displayed, check the following probable cause. When the problem is still occurring, replace the ESP control module. |
|
Inspection procedures
DTC Inspection
| 1. | Connect the GDS with the data link connector and turn the ignition switch ON. |
| 2. | Verify that the DTC code is output. |
| 3. | Is the DTC code output?
|
Check the power source circuit
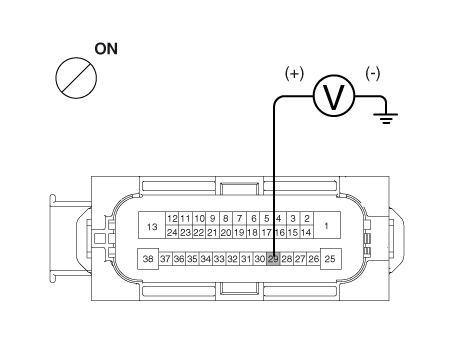
| 1. | Disconnect the connector from the ESP control module. |
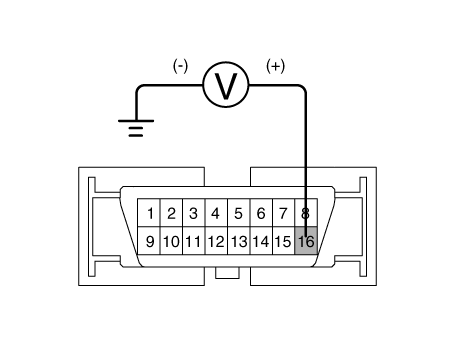
| 2. | Turn the ignition switch ON, measure the voltage between terminal 29 of the ESP control module harness side connector and body ground.
Is the voltage within specification?
|
Check the ground circuit
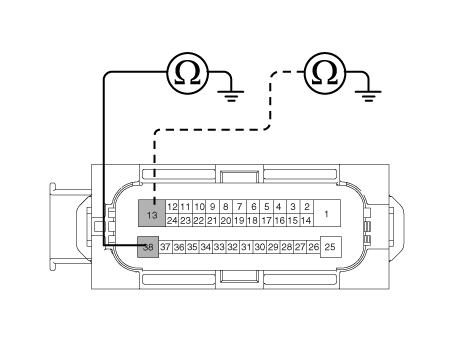
| 1. | Disconnect the connector from the ESP control module. |
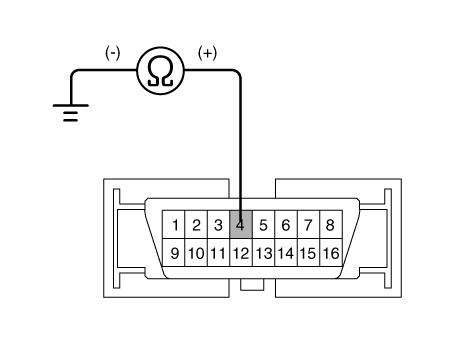
| 2. | Check for continuity between terminals 13, 38 of the ESP control module harness side connector and ground point. Is there continuity?
|
Check the wheel speed sensor circuit
| 1. | Refer to the DTC troubleshooting procedures. |
| 2. | Is it normal?
|
Check the hydraulic circuit for leakage
| 1. | Inspect leakage of the hydraulic lines. |
| 2. | Is it normal?
|

Detecting condition
| Trouble Symptoms | Possible Cause | ||||||||
| Brake operation varies depending on driving conditions and road surface conditions, so diagnosis can be difficult. However if a normal DTC is displayed, check the following probable cause. When the problem is still occurring, replace the ESP control module. |
|
Inspection procedures
DTC Inspection
| 1. | Connect the GDS with the data link connector and turn the ignition switch ON. |
| 2. | Verify that the DTC code is output. |
| 3. | Is the DTC code output?
|
Check the wheel speed sensor circuit
| 1. | Refer to the DTC troubleshooting procedures. |
| 2. | Is it normal?
|
Check the stop lamp switch circuit
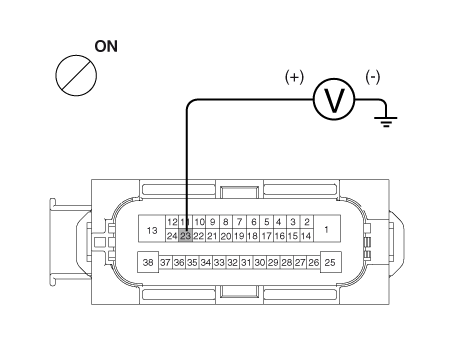
| 1. | Check that stop lamp lights up when brake pedal is depressed and turns off when brake pedal is released. |
| 2. | Measure the voltage between terminal 23 of the ESP control module harness side connector and body ground when brake pedal is depressed.
Is the voltage within specification?
|
Check the hydraulic circuit for leakage
| 1. | Refer to the hydraulic lines. |
| 2. | Inspection leakage of the hydraulic lines. |
| 3. | Is it normal?
|
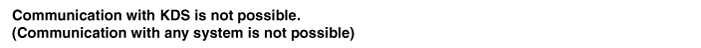
Detecting condition
| Trouble Symptoms | Possible Cause | ||||||
| Possible defect in the power supply system (including ground) for the diagnosis line. |
|
Inspection procedures
Check The Power Supply Circuit For The Diagnosis
| 1. | Measure the voltage between terminal 16 of the data link connector and body ground.
Is voltage within specification?
|
Check the ground circuit for the diagnosis
| 1. | Check for continuity between terminal 4 of the data link connector and body ground. Is there continuity?
|
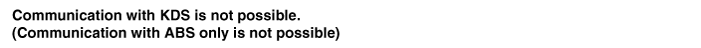
Detecting condition
| Trouble Symptoms | Possible Cause | ||||||
| When communication with GDS is not possible, the cause may be probably an open in the HECU power circuit or an open in the diagnosis output circuit. |
|
Inspection procedures
Check for Continuity in the CAN Line
| 1. | Disconnect the connector from the ESP control module. |
| 2. | Check for continuity between terminals 26, 14 of the ESP control module connector and 3, 11 of the data link connector. |
| 3. | Is there continuity?
|
Check the power source of ESP control module
| 1. | Disconnect the connector from the ESP control module. |
| 2. | Turn the ignition switch ON, measure the voltage between terminal 29 of the ESP control module harness side connector and body ground.
Is voltage within specification?
|
Check for poor ground
| 1. | Check for continuity between terminal 4 of the data link connector and ground point. |
| 2. | Is the electric current applied between groundings?
|

Detecting condition
| Trouble Symptoms | Possible Cause | ||||||||||
| When current flows in the HECU the ABS warning lamp turns from ON to OFF as the initial check. Therefore if the lamp does not light up, the cause may be an open in the lamp power supply circuit, a blown bulb, an open in the both circuits between the ABS warning lamp and the HECU, and the faulty HECU. |
|
Inspection procedures
Problem verification
| 1. | Disconnect the connector from the ESP control module and turn the ignition switch ON. |
| 2. | Does the ABS warning lamp light up?
|
Check the power source for the ABS warning lamp
| 1. | Disconnect the instrument cluster connector (M08) and turn the ignition switch ON. |
| 2. | Measure the voltage between terminal (M08) 39 of the cluster harness side connector and body ground.
|
| 3. | Is voltage within specification?
|
Check the CAN circuit resistance for ABS warning lamp
| 1. | Disconnect the instrument cluster connector (M08) and turn the ignition switch OFF. |
| 2. | Measure the resistance between terminal (M08) 32 and 33 of the cluster harness side connector.
|
| 3. | Is resistance within specification?
|
Check the CAN circuit wiring for ABS warning lamp
| 1. | Disconnect the instrument cluster connector (M08) and ESP HECU connector, and then turn the ignition switch OFF. |
| 2. | Check for continuity between terminal (M08) 32 of the cluster harness side connector and terminal 26 of ESP HECU harness side. Check for continuity between terminal (M08) 33 of the cluster harness side connector and terminal 14 of ESP HECU harness side.
|
| 3. | Is resistance within specification?
|

Detecting condition
| Trouble Symptoms | Possible Cause | ||||||||
| If the HECU detects trouble, it lights the ABS warning lamp while at the same time prohibiting ABS control. At this time, the HECU records a DTC in memory. Even though the normal code is output, the ABS warning lamp remains ON, then the cause may be probably an open or short in the ABS warning lamp circuit. |
|
Inspection procedures
Check DTC Output
| 1. | Connect the GDS to the 16P data link connector located behind the driver's side kick panel. |
| 2. | Check the DTC output using GDS. |
| 3. | Is DTC output?
|
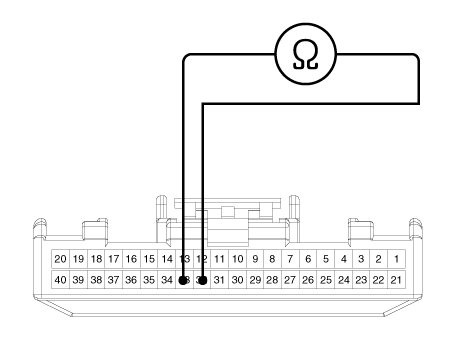
Check the CAN circuit resistance for ABS warning lamp
| 1. | Disconnect the instrument cluster connector (M08) and turn the ignition switch OFF. |
| 2. | Measure the resistance between terminal (M08) 32 and 33 of the cluster harness side connector.
|
| 3. | Is resistance within specification?
|
Check the CAN circuit wiring for ABS warning lamp
| 1. | Disconnect the instrument cluster connector (M08) and ESP HECU connector, and then turn the ignition switch OFF. |
| 2. | Check for continuity between terminal (M08) 32 of the cluster harness side connector and terminal 26 of ESP HECU harness side. Check for continuity between terminal (M08) 33 of the cluster harness side connector and terminal 14 of ESP HECU harness side.
|
| 3. | Is resistance within specification?
|
Schematic diagrams
| Terminal Function |
[EPB None Apply]
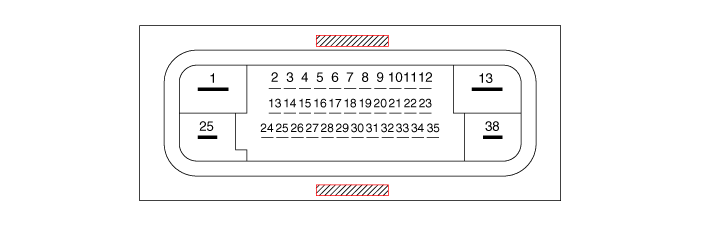
|
PIN No
|
Desciption
|
Current
| |
|
max
|
min
| ||
| 1 | Voltage supply for pump motor | 40A | 10 MΩ |
| 2 | Hazard switch | 1.2 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 3 | - | ||
| 4 | C-CAN HIGH | 100 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 5 | C-CAN LOW | 100 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 6 | |||
| 7 | P-CAN LOW | 100 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 8 | P-CAN High | 100 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 9 | Wheel speed sensor power voltage (RL) | 100 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 10 | Wheel speed sensor power voltage (RR) | 100 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 11 | Wheel speed sensor power voltage (FR) | 100 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 12 | Wheel speed sensor power voltage (FL) | 100 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 13 | Recirculation pump ground | 40A | 10 MΩ |
| 14 | - | ||
| 15 | Clutch Switch (MT Only) | 1.2 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 16 | DBC Switch | 1.2 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 17 | ESP Switch | 1.2 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 18 | - | ||
| 19 | Parking brake switch | 1.2 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 20 | - | ||
| 21 | Wheel speed sensor ground (RL) | 40 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 22 | Wheel speed sensor ground (RR) | 40 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 23 | Wheel speed sensor ground (FR) | 40 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 24 | Wheel speed sensor ground (FL) | 40 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 25 | Voltage supply for solenoid valves | 30A | 10 MΩ |
| 26 | - | ||
| 27 | - | ||
| 28 | - | ||
| 29 | - | ||
| 30 | Brake lamp switch | 1.2 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 31 | - | ||
| 32 | IGN 1 | 10mA | 50MΩ |
| 33 | - | ||
| 34 | HAC / BLA signal output | 1.2 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 35 | ESS signal output | 1.2 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 36 | - | ||
| 37 | Wheel speed sensor output (FR) | 50 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 38 | Ground for solenoid valves and ECU | 30A | 10 MΩ |
[EPB Apply]
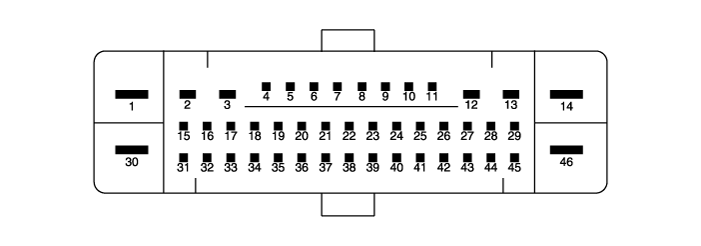
|
PIN No
|
Desciption
|
Current
|
Permit resistance
|
| 1 | Voltage supply for pump motor | 60A | 10 MΩ |
| 2 | RR EPB motor power | 15A | 10 MΩ |
| 3 | RR EPB motor ground | 15A | 10 MΩ |
| 4 | - | - | - |
| 4 | Clutch stroke sensor signal | - | - |
| 5 | Local CAN High | 40A | 250 MΩ |
| 6 | Electric parking brake signal 1 | 20 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 7 | Electric parking brake signal 2 | 20 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 8 | Electric parking brake signal 3 | 20 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 9 | Electric parking brake signal 4 | 20 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 10 | - | - | - |
| 11 | - | - | - |
| 12 | RL EPB motor ground | 15A | 10 MΩ |
| 13 | RL EPB motor power | 15A | 10 MΩ |
| 14 | Valves & ECU ground | 40A | 10 MΩ |
| 15 | DBC switch signal | 1.2 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 16 | - | ||
| 17 | ESP OFF switch signal | 1.2 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 18 | N Signal | 100 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 19 | Local CAN High | 100 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 20 | Local CAN Low | 100 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 21 | - | ||
| 22 | P-CAN LOW | 100 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 23 | P-CAN High | 100 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 24 | - | ||
| 25 | Wheel speed sensor supply voltage (RL) | 150 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 26 | Wheel speed sensor supply voltage (RR) | 150 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 27 | Wheel speed sensor supply voltage (FR) | 150 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 28 | Wheel speed sensor supply voltage (FL) | 150 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 29 | - | ||
| 30 | Voltage supply for solenoid valves | 40A | 10 MΩ |
| 31 | - | ||
| 32 | - | ||
| 33 | - | ||
| 34 | Auto holding ON/OFF switch signal | 1.2 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 35 | Brake light switch | 1.2 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 36 | HAC / BLA signal output | 1.2 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 37 | IGN 1 | 10 mA | 50 MΩ |
| 38 | ESS signal output | 1.2 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 39 | - | ||
| 40 | - | ||
| 41 | Wheel speed sensor ground (RL) | 40 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 42 | Wheel speed sensor ground (RR) | 40 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 43 | Wheel speed sensor ground (FR) | 40 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 44 | Wheel speed sensor ground (FL) | 40 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 45 | Wheel speed sensor power (FR) | 50 mA | 250 MΩ |
| 46 | Recirculation pump ground | 60A | 10 MΩ |
ESC (Electronic Stability Control) Module
Components and components location
| Components |
[LHD]
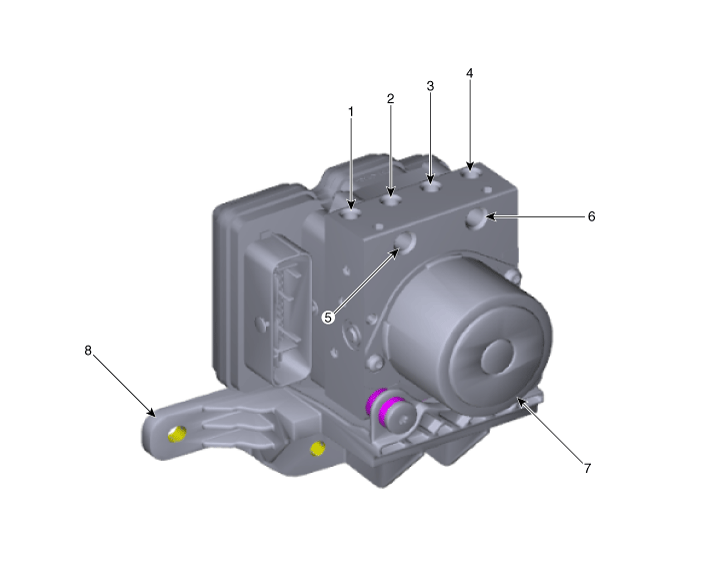
| 1. Front - right (FR) 2. Rear - left (RL) 3. Rear - right (RR) 4. Front - left (FL) | 5. MC2 6. MC1 7. ABS control module (HECU) 8. Bracket |
[RHD]
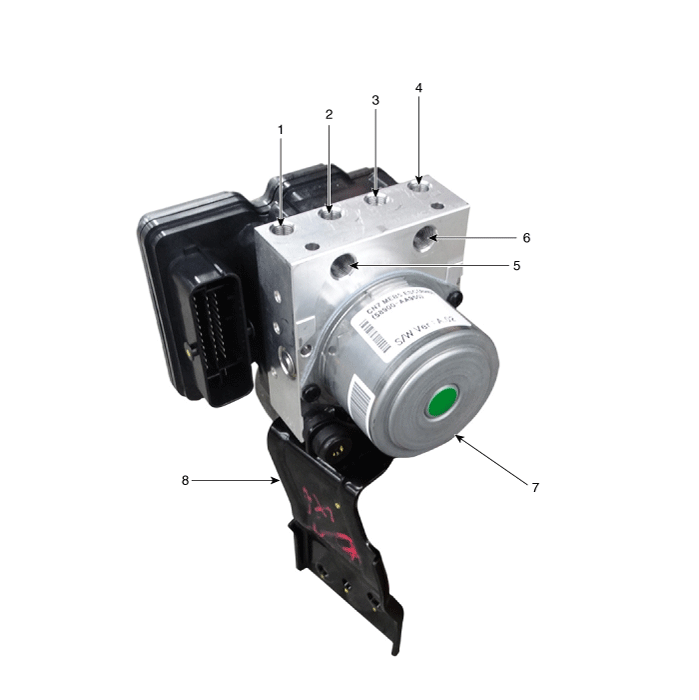
| 1. Front - right (FR) 2. Rear - left (RL) 3. Rear - right (RR) 4. Front - left (FL) | 5. MC2 6. MC1 7. ABS control module (HECU) 8. Bracket |
Repair procedures
| Removal |
[LHD]
| 1. | Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect the negative (-) battery cable. |
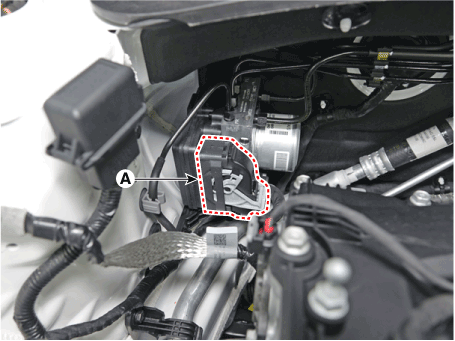
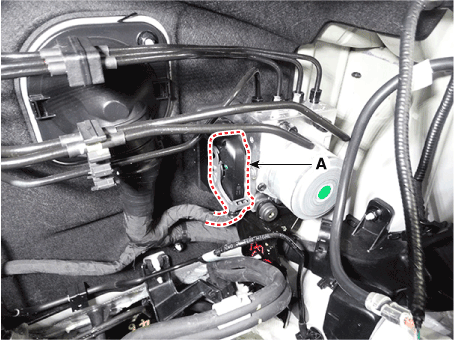
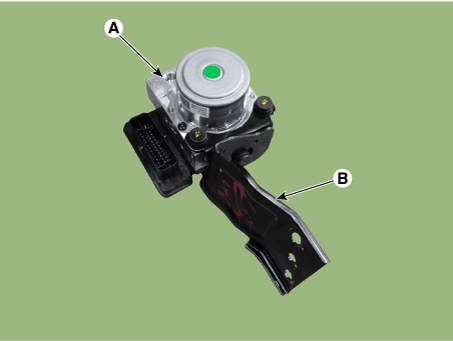
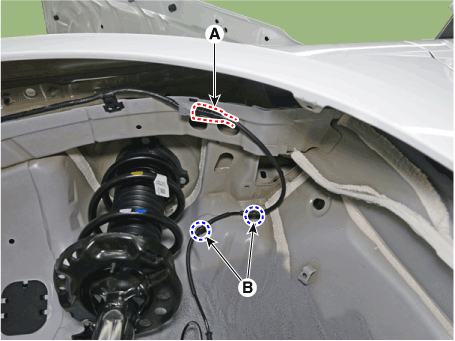
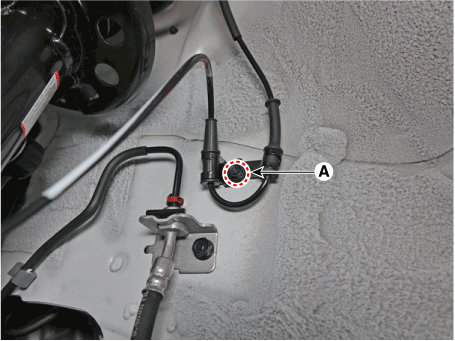
| 2. | Pull up the lock of the HECU connector and then disconnect the connector (A).
|
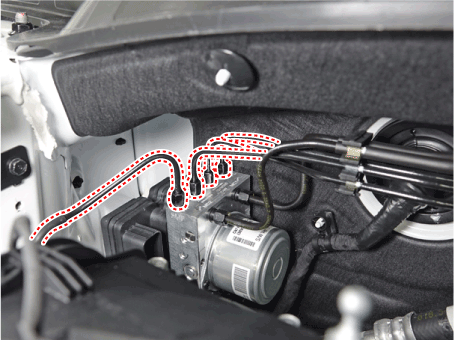
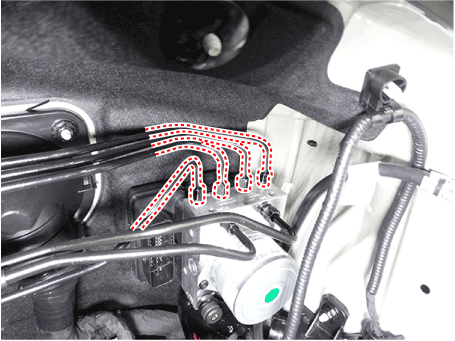
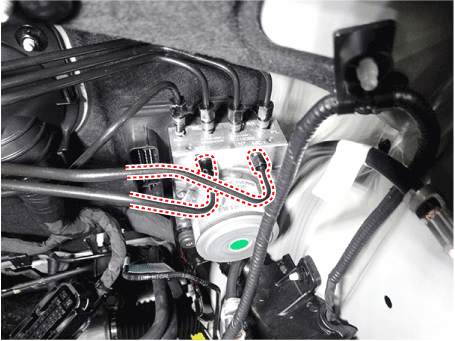
| 3. | Separate the brake tubes from the HECU by unlocking the nuts (6-ea) couterclockwise using a spanner.
|
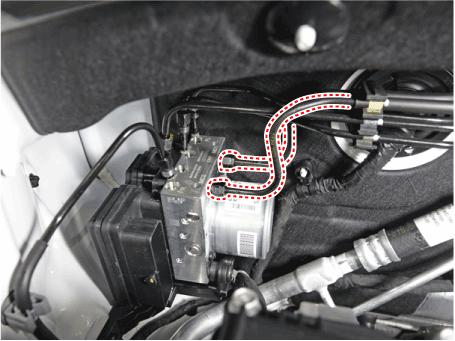
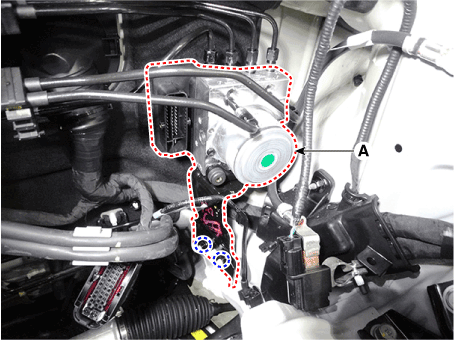
| 4. | Loosen the ABS control module mounting nut and then remove the ABS control module (A) from the vehicle.
|
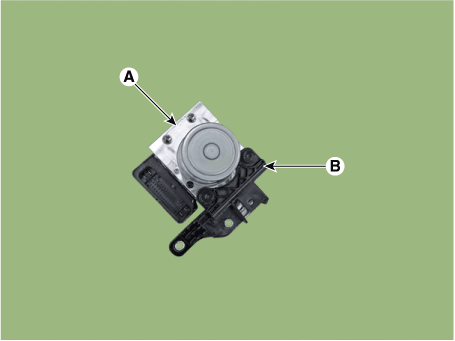
| 5. | Separate the bracket (B) after remove the mounting bolt from the HECU (A).
|
[RHD]
| 1. | Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect the negative (-) battery cable. |
| 2. | Remove the battery and battery tray. (Refer to Engine Electrical System - "Battery") |
| 3. | Pull up the lock of the HECU connector and then disconnect the connector (A).
|
| 4. | Separate the brake tubes from the HECU by unlocking the nuts (6-ea) couterclockwise using a spanner.
|
| 5. | Loosen the ABS control module mounting nut and then remove the ESC control module (A) from the vehicle.
|
| 6. | Separate the bracket (B) after remove the mounting bolt from the HECU (A).
|
| Installation |
| 1. | To install, reverse the removal procedure. |
| 2. | After installation, bleed the brake system. (Refer to Brake System - "Brake Bleeding Prcoedures") |
| Adjustment |
Perform diagnostic procedure by using diagnostic device as shown below.
| 1. | Connect self-diagnosis connector (16pins) located under the driver side crash pad to self-diagnosis device, and then turn the self-diagnosis device after key is ON. |
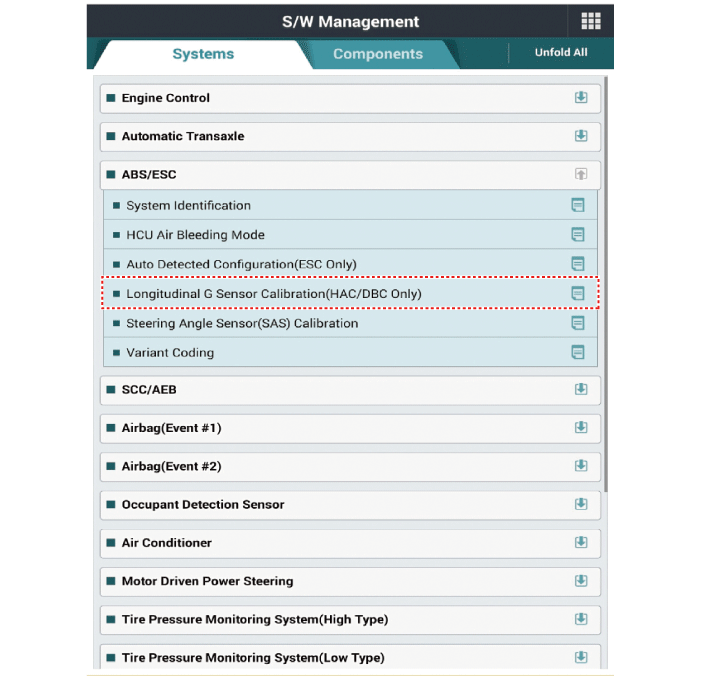
| 2. | Select the "vehicle model" and "ESP/ESC" on GDS vehicle selection screen, then select OK. [Variant Code Reset]
[Variant Coding]
[Longitudinal G Sensor Calibration]
|
ESC OFF Switch
Description and operation
| Description |
| 1. | The ESP OFF switch is for the user to turn off the ESP system. |
| 2. | The ESP OFF lamp is on when ESP OFF switch is engaged. |
Repair procedures
| Removal |
| 1. | Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect the negative (-) battery cable. |
| 2. | Remove the crash pad lower pannel. (Refer to Body - "Crash Pad Lower Pannel") |
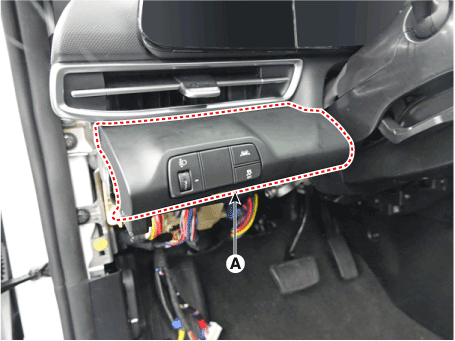
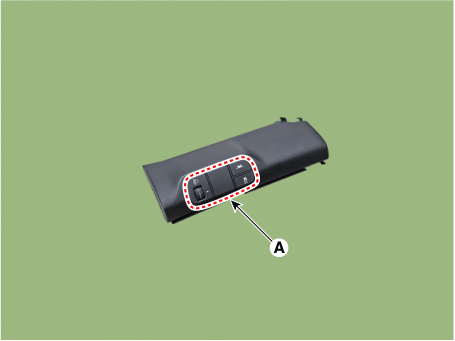
| 3. | Loosen the screw and than removing the ESC OFF switch (A).
|
| 4. | Disconnect the crash pad lower switch connector (A).
|
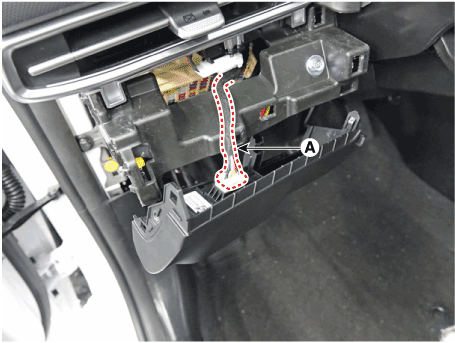
| 5. | Remove the VDC OFF switch (A) after loosening screw.
|
Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Components and components location
| Components |
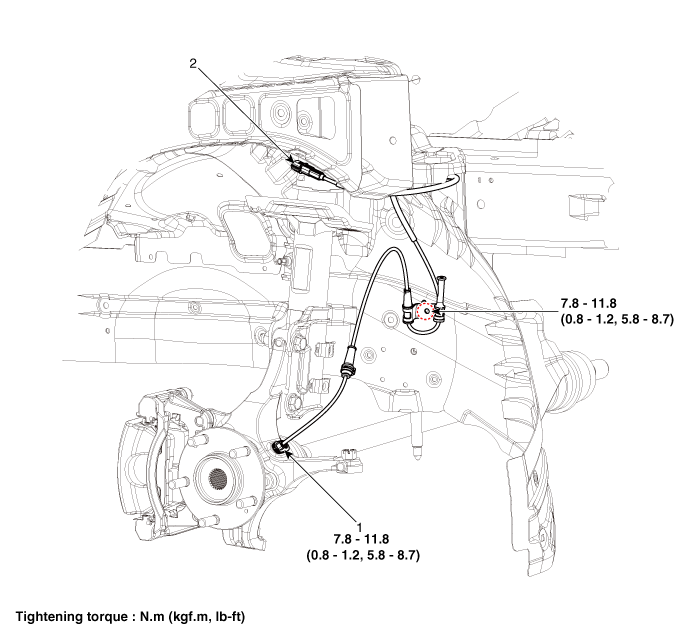
| 1. Front wheel speed sensor | 2. Front wheel speed sensor connector |
Repair procedures
| Removal |
| 1. | Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect the negative (-) battery cable. |
| 2. | Loosen the wheel nuts slightly. Raise the vehicle, and make sure it is securely supported. |
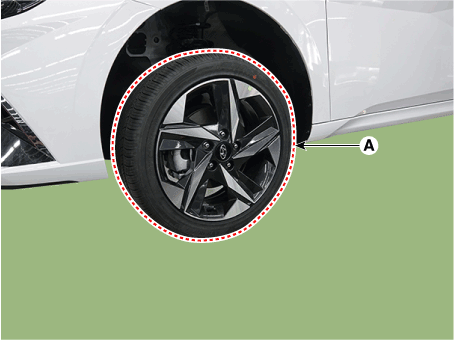
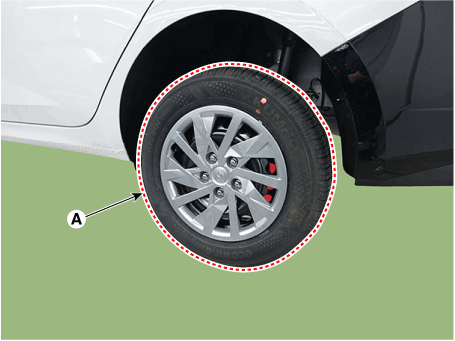
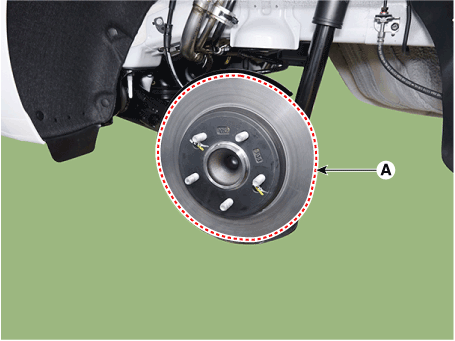
| 3. | Remove the rear wheel and tire (A) from the rear hub.
|
| 4. | Remove the front wheel guard. (Refer to Body - "Front Wheel Guard") |
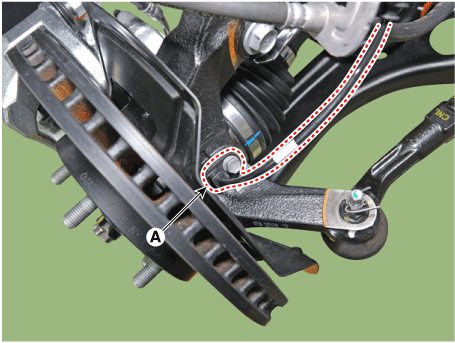
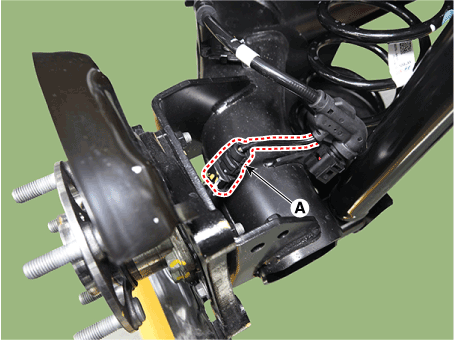
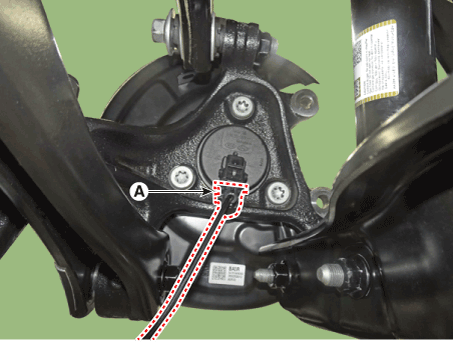
| 5. | Disconnect the front wheel speed sensor connector (A) and then remove the fixing clip (B).
|
| 6. | Remove the front wheel speed sensor cable braket bolt (A).
|
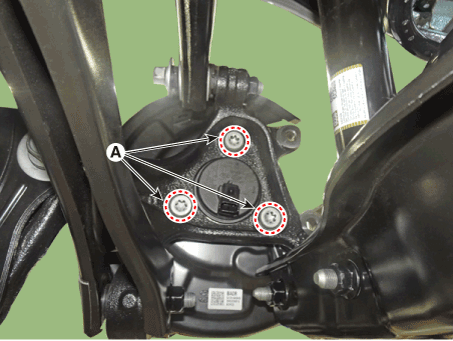
| 7. | Remove the wheel speed sensor (A) from the Knuckle after loosening the mounting bolt.
|
| Installation |
| 1. | To install, reverse the removal procedure. |
| Inspection |
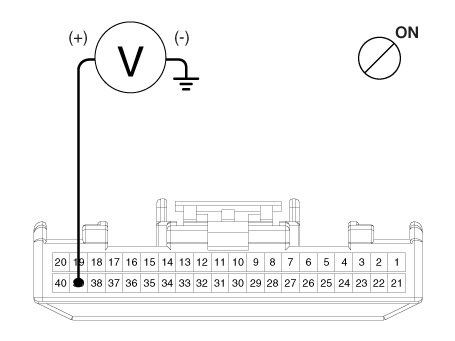
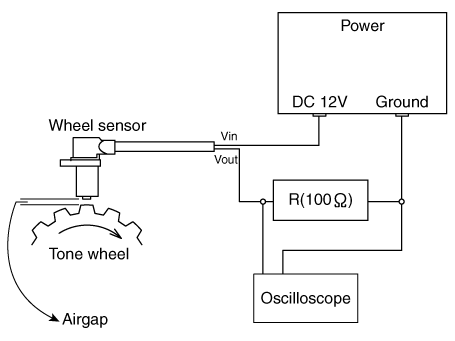
| 1. | Measure the output voltage between the terminal of the wheel speed sensor and the body ground.
|
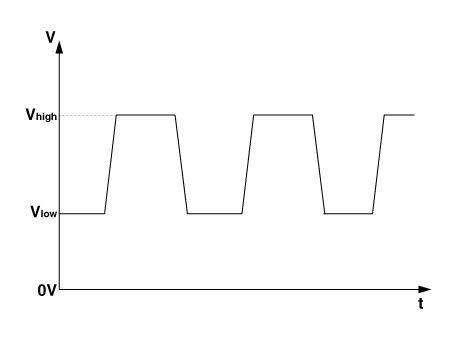
| 2. | Compare the change of the output voltage of the wheel speed sensor to the normal change of the output voltage as shown below.
|
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Components and components location
| Components |
[Rear torsion beam disc brake type]
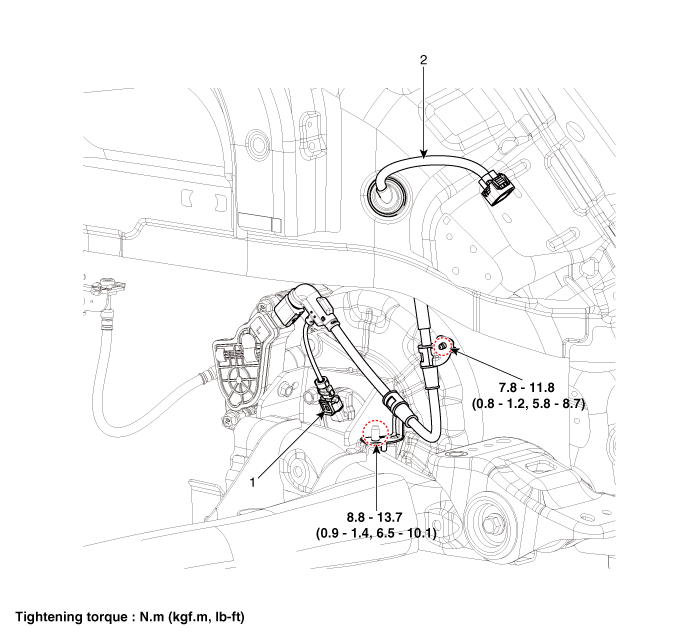
| 1. Rear wheel speed sensor | 2. Rear wheel speed sensor connector |
[Rear multi link disc brake type]
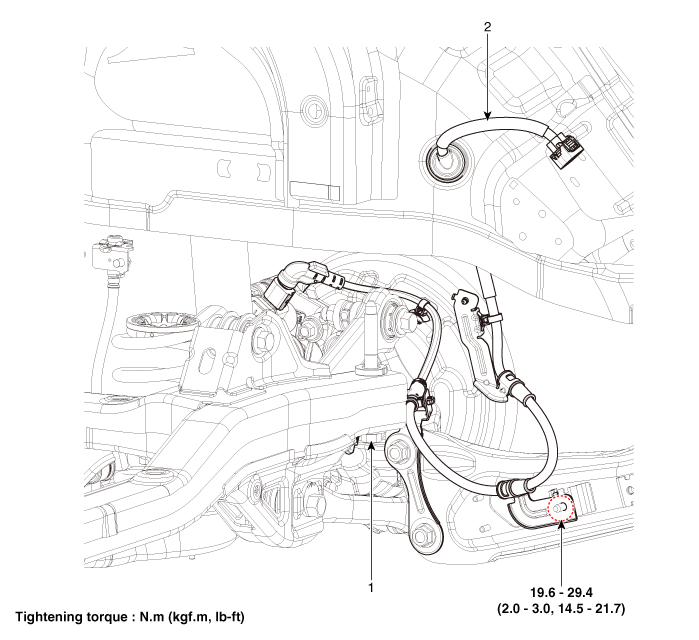
| 1. Rear wheel speed sensor | 2. Rear wheel speed sensor connector |
[Rear drum brake type]
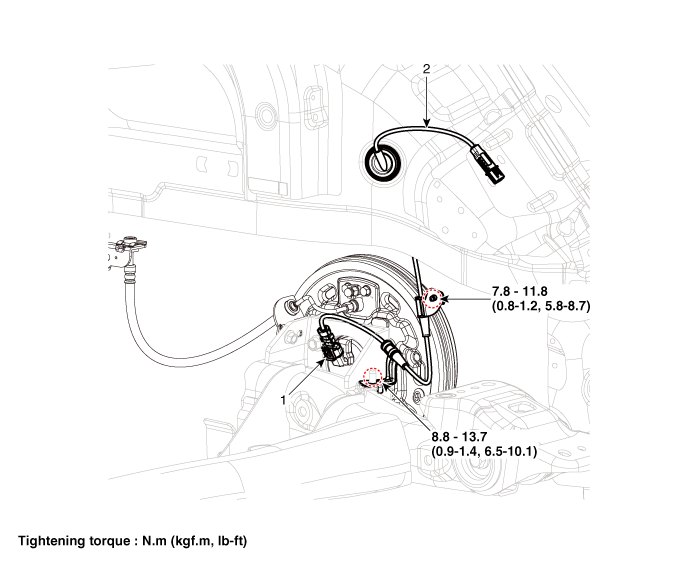
| 1. Rear wheel speed sensor | 2. Rear wheel speed sensor connector |
Repair procedures
| Removal |
[Rear torsion beam disc brake type]
| 1. | Loosen the wheel nuts slightly. Raise the vehicle, and make sure it is securely supported. |
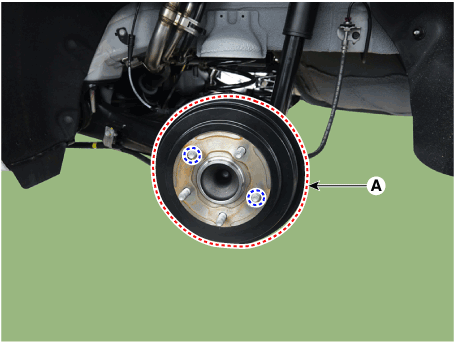
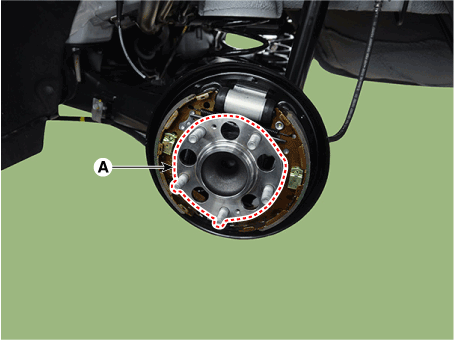
| 2. | Remove the rear wheel and tire (A) from the rear hub.
|
| 3. | Remove the rear brake caliper. (Refer to Brake System - "Rear Disc Brake") |
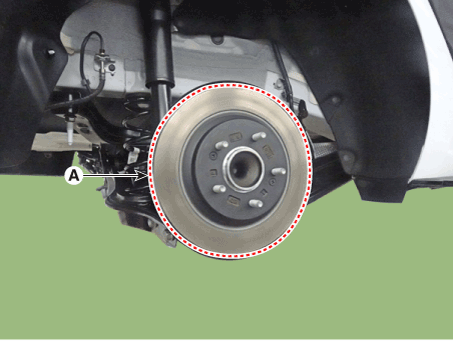
| 4. | Remove the rear brake disc (A).
|
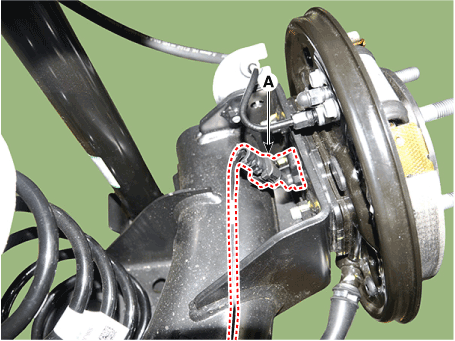
| 5. | Disconnect the rear wheel speed sensor connector (A).
|
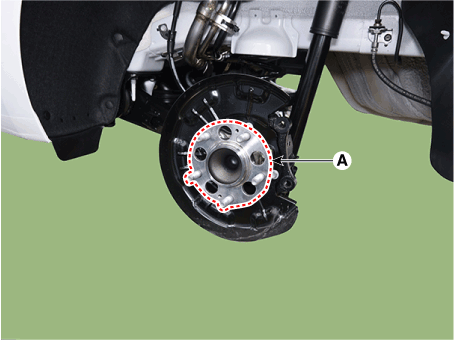
| 6. | Remove the hub bearing assembly (A) after loosening the mounting bolts.
|
[Rear multi link disc brake type]
| 1. | Loosen the wheel nuts slightly. Raise the vehicle, and make sure it is securely supported. |
| 2. | Remove the rear wheel and tire (A) from the rear hub.
|
| 3. | Remove the rear brake caliper. (Refer to Brake System - "Rear Disc Brake") |
| 4. | Remove the rear brake disc (A) after loosening the mounting screw.
|
| 5. | Disconnect the rear wheel speed sensor connector (A).
|
| 6. | Remove the hub bearing assembly after loosening the hub bearing mounting bolts (A).
|
[Rear drum brake type]
| 1. | Loosen the wheel nuts slightly. Raise the vehicle, and make sure it is securely supported. |
| 2. | Remove the rear wheel and tire (A) from the rear hub.
|
| 3. | Disconnect the rear wheel speed sensor connector (A).
|
| 4. | Loosen the screw and then remove the rear drum brake (A).
|
| 5. | Loosen the hub mounting bolts and then remove the hub (A) from the torsion beam.
|
| Replacement |
| 1. | Remove the rear wheel hub bearing assembly. (Refer to Driveshaft and Axle - "Rear Hub - Carrier") |
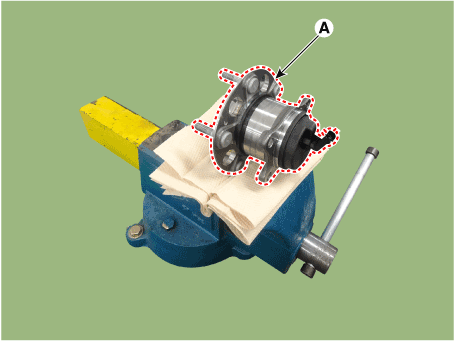
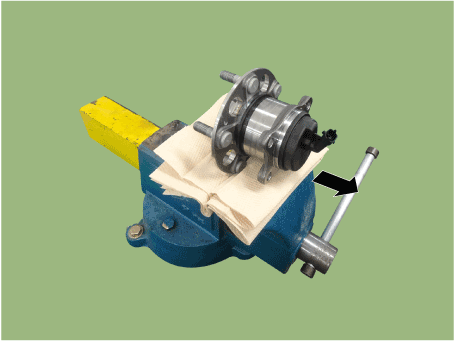
| 2. | Fix the rear hub bearing assembly (A) on the vise.
|
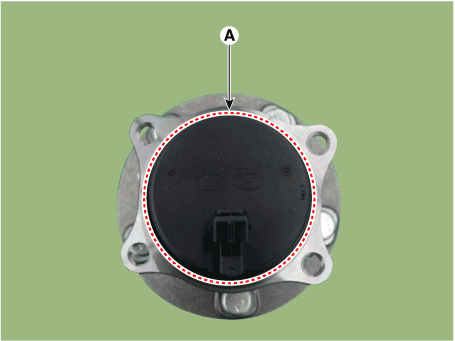
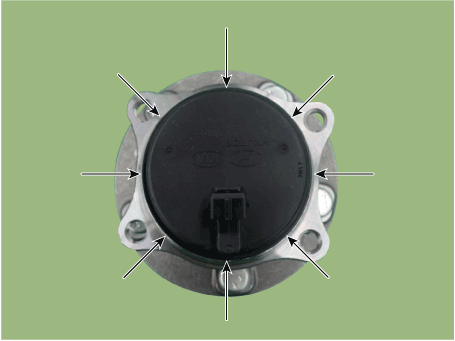
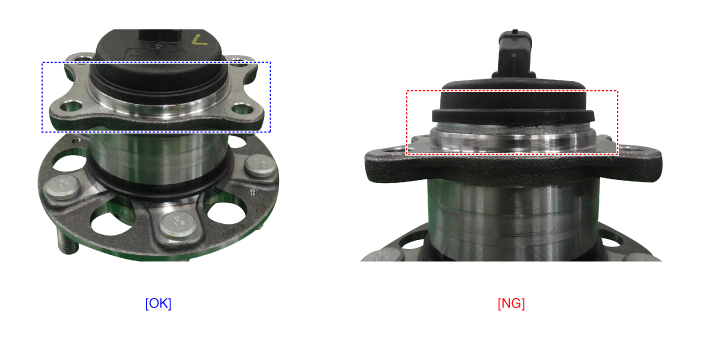
| 3. | Check the direction of the sensor cap (A).
|
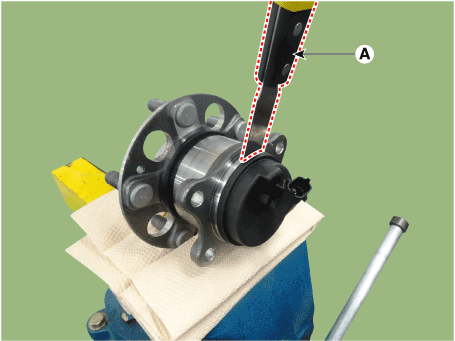
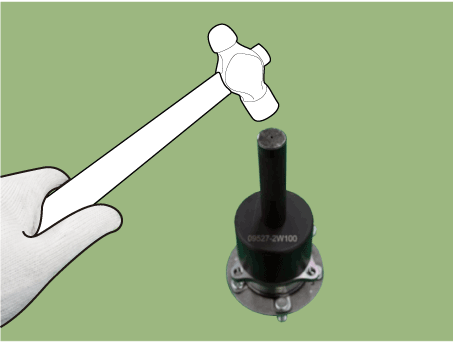
| 4. | Remove the sensor cap by hammering on a gap between sensor cap and hub bearing assembly using a scraper (A).
|
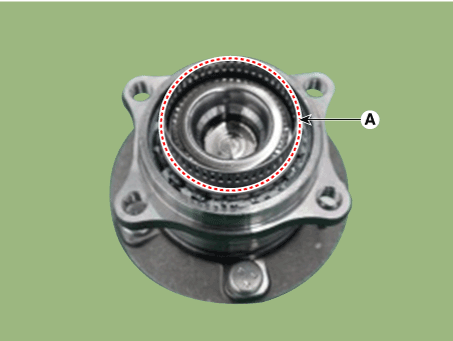
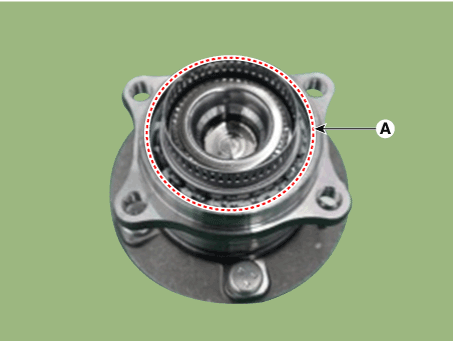
| 5. | Check if distorted or damaged the tone wheel or encoder (A).
|
| 6. | Position the sensor cap to the same direction of sensor cap connector (A) as you checked before removing.
|
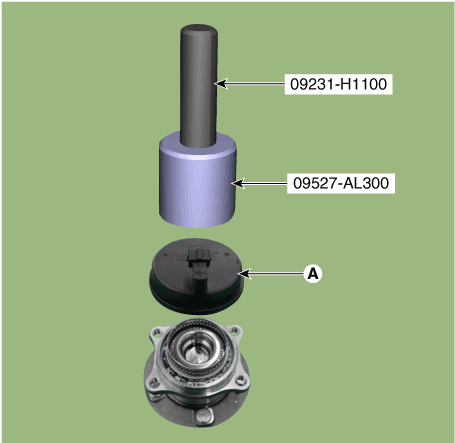
| 7. | Install the sensor cap (A) with the special service tool (09527-AL300).
|
| 8. | Install the rear wheel hub bearing assembly. (Refer to Driveshaft and Axle - "Rear Hub - Carrier") |
| Installation |
| 1. | To install, reverse the removal procedure. |
| Inspection |
| 1. | Measure the output voltage between the terminal of the wheel speed sensor and the body ground.
|
| 2. | Compare the change of the output voltage of the wheel speed sensor to the normal change of the output voltage as shown below.
|
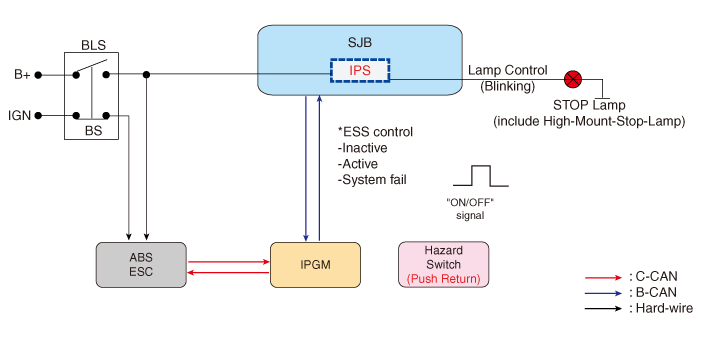
Emergency Signal System
Description and operation
| Description |
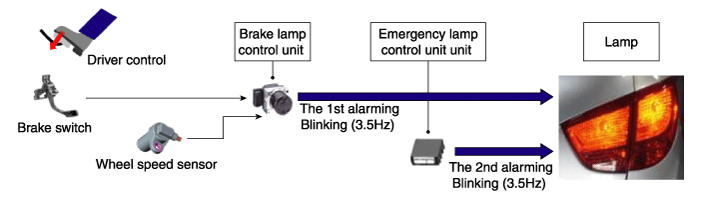
Introduction of Quick Brake Warning System (ESS)
In case of quick brake by driver, the brake lamp or turn signal is blinked to warn against the vehicle at rear.
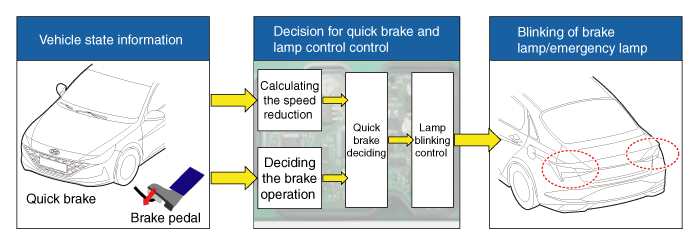
| 1. | Basic function (Blinking the brake lamp/emergency lamp)
|
| 2. | Additional function (Blinking the turn signal)
|
System Configuration
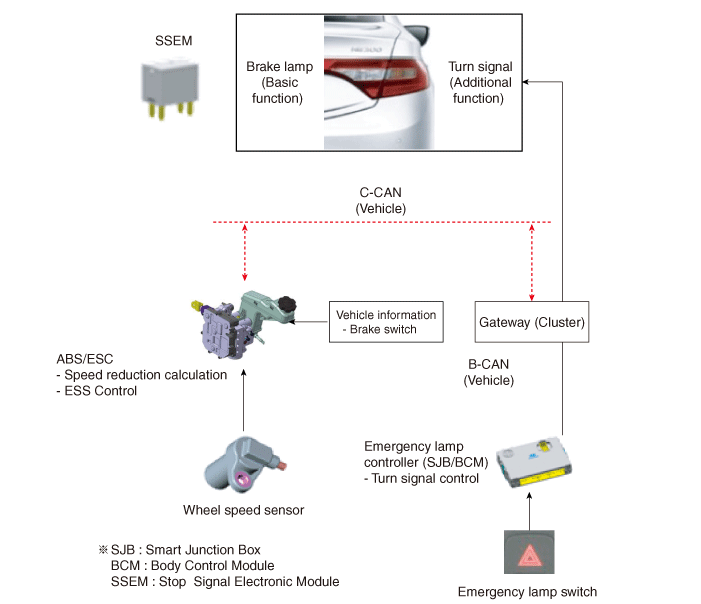
ESS Circuit Diagram