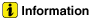Description and operation
The charging system included a battery, an alternator with a built-in regulator, and the charging indicator light and wire.
The Alternator has eight built-in diodes, each rectifying AC current to DC current.
Therefore, DC current appears at alternator "B" terminal.
In addition, the charging voltage of this alternator is regulated by the battery voltage detection system.
The alternator is regulated by the battery voltage detection system. The main components of the alternator are the rotor, stator, rectifier, capacitor brushes, bearings and V-ribbed belt pulley. The brush holder contains a built-in electronic voltage regulator.
| Alternator Management System (AMS) |
Alternator management system controls the charging voltage set point in order to improve fuel economy, manage alternator load under various operating conditions, keep the battery charged, and protect the battery from over-charging. ECM controls generating voltage by duty cycle (charging control, discharging control, normal control) based on the battery conditions and vehicle operating conditions.
The system conducts discharging control when accelerating a vehicle. Vehicle reduces an alternator load and consumes an electric power form a battery.
The system conducts charging control when decelerating a vehicle. Vehicle increases an alternator load and charges a battery.
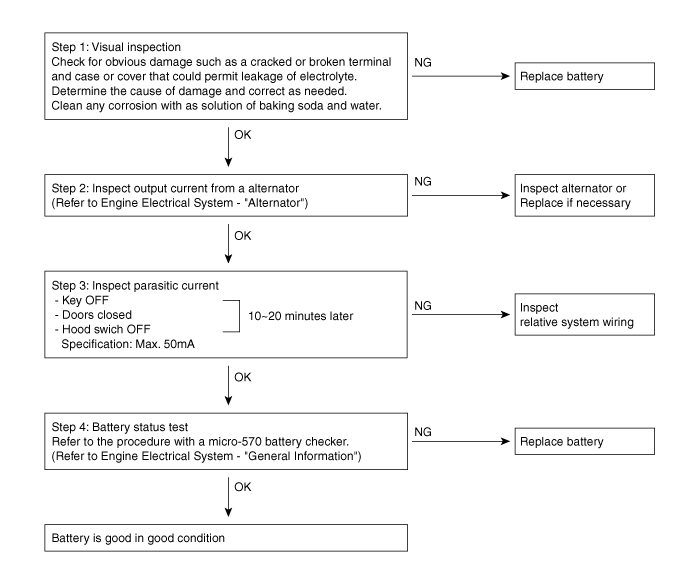
Troubleshooting
Symptom
|
Suspect area
|
Remedy
|
Charging warning indicator does not light with ignition switch "ON" and engine off.
| Fuse blown
| Check fuses
|
Light burned out
| Replace light
|
Wiring connection loose
| Tighten loose connection
|
Electronic voltage regulator
| Disconnect the voltage regulator to see if light turns off. If light turns off, replace voltage regulator.
|
Charging warning indicator does not go out with engine running. (Battery requires frequent recharging)
| Drive belt loose or worn
| Adjust belt tension or replace belt
|
Battery cable loose, corroded or worn
| Inspect cable connection, repair or replace cable
|
Electronic voltage regulator or alternator
| Disconnect the voltage regulator or alternator to see if light turns off. If light turns off, replace voltage regulator.
|
Wiring
| Repair or replace wiring
|
Overcharge
| Electronic voltage regulator
| Disconnect the voltage regulator to see if light turns off. If light turns off, replace voltage regulator.
|
Voltage sensing wire
| Repair or replace wiring
|
Discharge
| Drive belt loose or worn
| Adjust belt tension or replace belt
|
Wiring connection loose or short circuit
| Inspect wiring connection, repair or replace wiring
|
Electronic voltage regulator or alternator
| Disconnect the voltage regulator or alternator to see if light turns off. If light turns off, replace voltage regulator.
|
Poor grounding
| Inspect ground or repair
|
Worn battery
| Replace battery
|
Repair procedures
| •
| Battery efficiency inspection |
| •
| Battery voltage inspection |
| •
| Charging voltage insptection |
| •
| Terminal tightening state inspection |
| •
| Engine/ transaxle ground state inspection |
| •
| Wiring hareness ground state inspection |
| •
| Electrical Specified Value Inspection |
| •
| Vehicle parasitic current inspection |
| •
| Inspect the battery capacity |
Battery Efficiency Inspection
| •
| Check that the battery cables are connected to the correct terminals. |
| •
| Disconnect the battery cables when the battery is given a quick charge. |
| •
| Never disconnect the battery while the engine is running. |
|
| •
| Inspect the battery test using the load tester and battery tester. |
|
Battery Voltage Inspection
| 1. | After having driven the vehicle and in the case that 20 minutes have not passed after having stopped the engine, turn the ignition switch ON and turn on the electrical system (headlamp, blower motor, rear defogger etc.) for 60 seconds to remove the surface charge. |
| 2. | Turn the ignition switch OFF and turn off the electrical systems. |
| 3. | Measure the battery voltage between the negative (-) and positive (+) terminals of the battery. Standard voltage : About 12.5 - 12.9V (20°C) |
If the voltage is less than specification, charge the battery. |
Charging Voltage Insptection
| 2. | Turn ON the electrical systems. |
| 3. | While keeping the engine speed at 2,500rpm. |
| 4. | Measure the battery voltage between the negative (-) and positive (+) terminals of the battery. Standard voltage : About 13.5 - 14.5V (20°C) |
If the voltage is less than specification, charge the battery. |
General Inspection
| 1. | Check that the battery terminals are not loose or corroded. (Refer to Charging System - "Battery") |
| 2. | Check the fuses for continuity. | (1) | Check the alternator fuse for continuity. 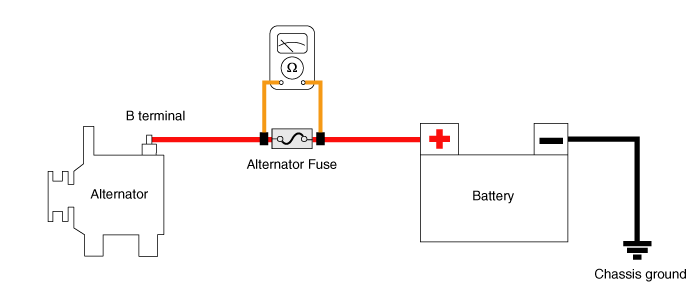
|
| (2) | Measure the voltage as shown in the image below. Standard value : About 0V |
|
| (3) | If the alternator fuse blown, below replace the alternator fuse. | a. | Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect the battery negative (-) terminal. |
| b. | Remove the battery positive (+) cable mounting nuts. |
| c. | Remove the battery positive (+) cable. |
| d. | Replace the norminal alternator fuse or battery cable. |
| e. | Install in the reverse order of removal. |
|
| (4) | Check the battery sensor fuse for continuity. |
| (5) | If the alternator fuse blown, replace the battery sensor fuse. |
| (6) | Measure the voltage as shown in the image below. Standard Value : About 0V |
|
|
| 3. | Inspect Drive Belt | (1) | Visually check the belt for excessive wear, frayed cords etc. If any defect has been found, replace the drive belt. | •
| Cracks on the rib side of a belt are considered acceptable. If the belt has chunks missing from the ribs, it should be replaced. |
|
|
|
| 4. | Drive belt tension measurement and adjustment. (Refer to Engine Mechanical System - "Drive Belt") |
| 5. | Visually Check Alternator Wiring And Listen For Abnormal Noises | (1) | Check that the wiring is in good condition. |
| (2) | Check that there is no abnormal noise from the alternator while the engine is running. |
|
| 6. | Check Discharge Warning Light Circuit | (1) | Warm up the engine and then turn it off. |
| (2) | Turn off all accessories |
| (3) | Turn the ignition switch "ON". Check that the discharge warning light is lit. |
| (4) | Start the engine. Check that the light is lit.. If the light does not go off as specified, troubleshoot the discharge light circuit. |
|
Terminal Tightening State Inspection
| •
| Alternator B+ terminal state |
| •
| Alternator B+ termina tightening nut |
| •
| Battery positive (+) terminal state |
| •
| Battery positive (+) terminal tightening nut state |
| •
| Battery negative (-) terminal state |
| •
| Battery negative (-) terminal tightening nut state |
| •
| Battery negative (-) terminal mounting bolt tightening state (Chassis ground) |
| •
| Battery sensor negative (-) terminal state (With battery sensor) |
| •
| Battery sensor negative (-) terminal tightening nut state (With battery sensor) |
| •
| Battery sensor negative (-) terminal mounting bolt tightening state (Chassis ground) [With battery sensor] |
| •
| Engine room fuse & relay box positive (+) harness state |
| •
| Engine room fuse & relay box positive (+) harness tightening nut state |
| •
| Check the status of ground fault by chassis paint |
|
| Inspection Component Location |
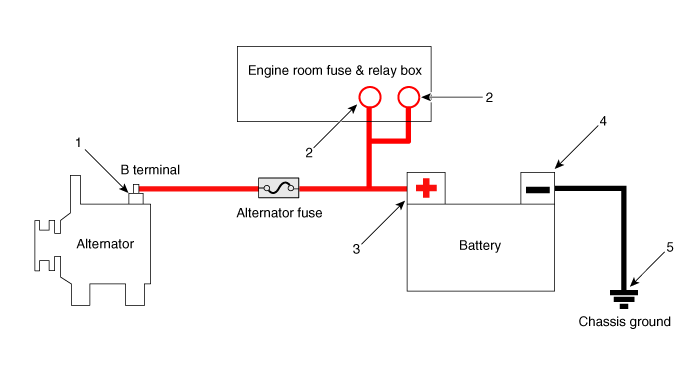
1. Alternator B+ terminal
2. Engine room fuse & relay box positive (+) terminal
3. Battery negative (+) terminal
| 4. Battery negative (-) terminal
5. Chassis ground
|
Engine/ Transaxle Ground State Inspection
| •
| Mounting bolt tightening state (Chassis) |
| •
| Mounting bolt tightening state (Engine) |
| •
| Check the status of ground fault by chassis paint |
|
Wiring Hareness Ground State Inspection
| •
| Mounting bolt tightening state (Chassis) |
| •
| Mounting bolt tightening state (Engine) |
| •
| Check the status of ground fault by chassis paint |
|
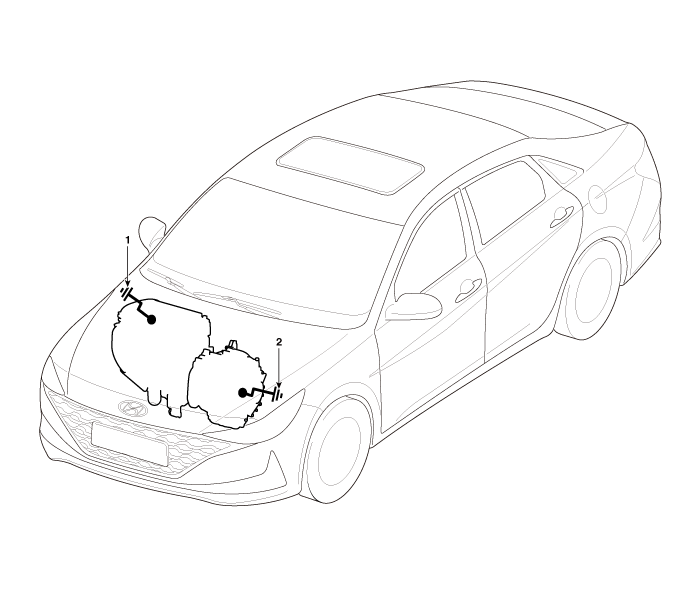
1. Engine ground (Engine ↔ Chassis)
2. Transaxle ground (Transaxle ↔ Chassis)
| |
| •
| Check the ground point. (Refer to ETM Harness Layout - "Ground Point") |
|
Electrical Specified Value Inspection (Using the Voltmeter and Ammeter)
| 1. | Voltage Drop Test Of Alternator Output Wire This test determines whether or not the wiring between the alternator "B" terminal and the battery (+) terminal is good by the voltage drop method. | (1) | Preparation | a. | Turn the ignition switch to "OFF". |
| b. | Disconnect the output wire from the alternator "B" terminal. Connect the (+) lead wire of ammeter to the "B" terminal of alternator and the (-) lead wire of ammeter to the output wire. Connect the (+) lead wire of voltmeter to the "B" terminal of alternator and the (-) lead wire of voltmeter to the (+) terminal of battery. 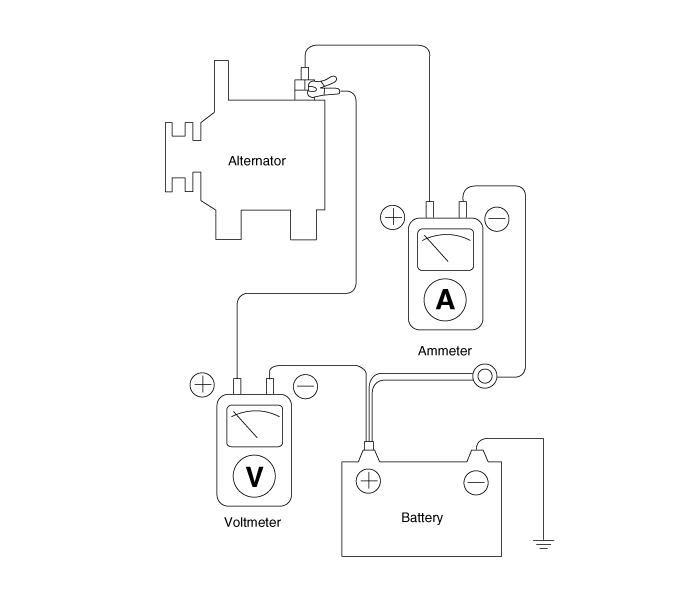
|
|
| (2) | Test | b. | Turn on the headlamps and blower motor, and set the engine speed until the ammeter indicates 20A.And then, read the voltmeter at this time. |
|
| (3) | Result | a. | The voltmeter may indicate the standard value. Standard value : 0.2V max |
|
| b. | If the value of the voltmeter is higher than expected (above 0.2V max.), poor wiring is suspected. In this case check the wiring from the alternator "B" terminal to the battery (+) terminal. Check for loose connections, color change due to an over-heated harness, etc. Correct them before testing again. |
| c. | Upon completion of the test, set the engine speed at idle.Turn off the headlamps, blower motor and the ignition switch. |
|
|
| 2. | Output Current Test This test determines whether or not the alternator gives an output current that is equivalent to the normal output. | (1) | Preparation | a. | Prior to the test, check the following items and correct as necessary. Check the battery installed in the vehicle to ensure that it is good condition. The battery checking method is described in the section "Battery". The battery that is used to test the output current should be one that has been partially discharged. With a fully charged battery, the test may not be conducted correctly due to an insufficient load. Check the tension of the alternator drive belt. The belt tension check method is described in the section "Inspect drive belt". |
| b. | Turn off the ignition switch. |
| c. | Disconnect the battery ground cable. |
| d. | Disconnect the alternator output wire from the alternator "B" terminal. |
| e. | Connect a DC ammeter (0 to 150A) in series between the "B" terminal and the disconnected output wire. Be sure to connect the (-) lead wire of the ammeter to the disconnected output wire. | •
| Tighten each connection securely, as a heavy current will flow. Do not rely on clips. |
|
|
| f. | Connect a voltmeter (0 to 20V) between the "B" terminal and ground. Connect the (+) lead wire to the alternator "B" terminal and (-) lead wire to a good ground. |
| g. | Connect the battery ground cable. |
| h. | Leave the engine hood open. 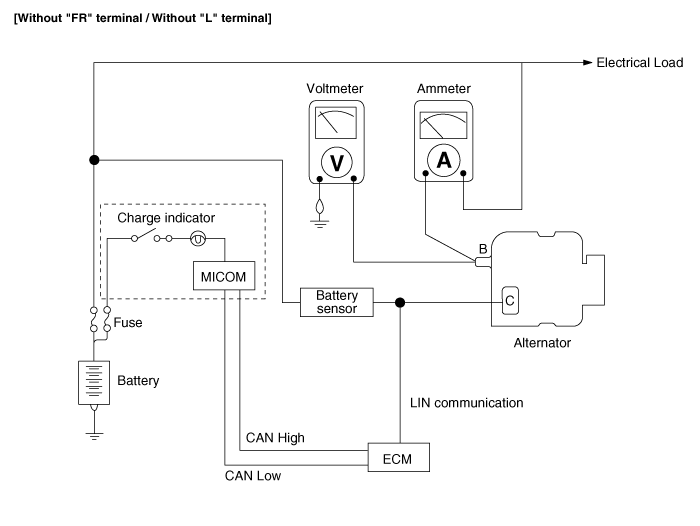
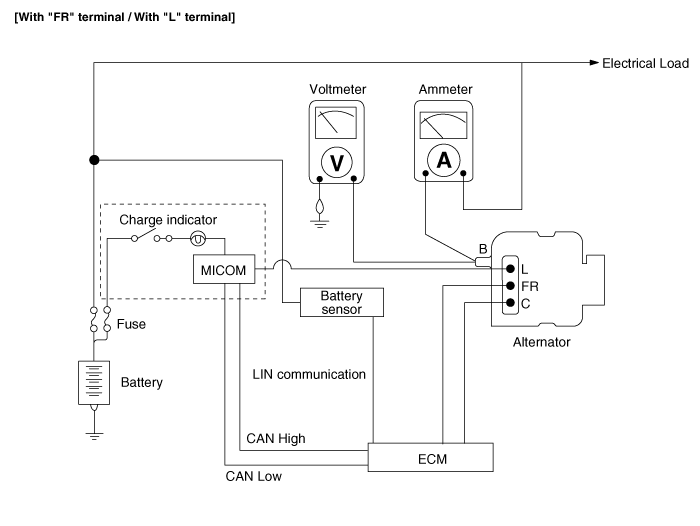
|
|
| (2) | Test | a. | Check to see that the voltmeter reads as the same value as the battery voltage. If the voltmeter reads 0V, and the open circuit in the wire between alternator "B" terminal and battery (+) terminal or poor grounding is suspected. |
| b. | Start the engine and turn on the headlamps. |
| c. | Set the headlamps to high beam and the heater blower switch to HIGH, quickly increase the engine speed to 2,500rpm and read the maximum output current value indicated by the ammeter. | •
| After the engine start up, the charging current quickly drops. Therefore, the above operation must be done quickly to read the maximum current value correctly. |
|
|
|
| (3) | Result | a. | The ammeter reading must be higher than the limit value. If it is lower but the alternator output wire is in good condition, remove the alternator from the vehicle and test it. Limit value : Rated current 60% |
| •
| The nominal output current value is shown on the nameplate affixed to the alternator body. |
|
| •
| The output current value changes with the electrical load and the temperature of the alternator itself. Therefore, the nominal output current may not be obtained. If such is the case, keep the headlamps on the cause discharge of the battery, or use the lights of another vehicle to increase the electrical load. The nominal output current may not be obtained if the temperature of the alternator itself or ambient temperature is too high. In such a case, reduce the temperature before testing again. |
|
|
| b. | Upon completion of the output current test, lower the engine speed to idle and turn off the ignition switch |
| c. | Disconnect the battery negative (-) terminal. |
| d. | Remove the ammeter and voltmeter and the engine tachometer. |
| e. | Connect the alternator output wire to the alternator "B" terminal. |
| f. | Connect the battery negative (-) terminal. |
|
|
| 3. | Regulated Voltage Test The purpose of this test is to check that the electronic voltage regulator controls voltage correctly. | (1) | Preparation | a. | Prior to the test, check the following items and correct if necessary. Check that the battery installed on the vehicle is fully charged. The battery checking method is described in the section "Battery". Check the alternator drive belt tension. The belt tension check method is described in the section "Inspect drive belt". |
| b. | Turn ignition switch to "OFF". |
| c. | Disconnect the battery negative (-) terminal. |
| d. | Connect a digital voltmeter between the "B" terminal of the alternator and ground. Connect the (+) lead of the voltmeter to the "B" terminal of the alternator. Connect the (-) lead to good ground or the battery (-) terminal. |
| e. | Disconnect the alternator output wire from the alternator "B" terminal. |
| f. | Connect a DC ammeter (0 to 150A) in series between the "B" terminal and the disconnected output wire.Connect the (-) lead wire of the ammeter to the disconnected output wire. |
| g. | Connect the battery negative (-) terminal. 

|
|
| (2) | Test | a. | Turn on the ignition switch and check to see that the voltmeter indicates the following value. Voltage : Battery voltage |
If it reads 0V, there is an open circuit in the wire between the alternator "B" terminal and the battery and the battery (-) terminal. |
| b. | Start the engine. Keep all lights and accessories off. |
| c. | Run the engine at a speed of about 2,500 rpm and read the voltmeter when the alternator output current drops to 10A or less |
|
| (3) | Result | a. | If the voltmeter reading doesn't agree with thestandard value, the voltage regulator or thealternator is faulty. Regulated Voltage : 11.7 - 15.3V |
|
| b. | If the voltmeter reading doesn't agree with thestandard value, the voltage regulator or thealternator is faulty. |
| c. | Disconnect the battery negative (-) terminal. |
| d. | Remove the voltmeter and ammeter. |
| e. | Connect the alternator output wire to the alternator "B" terminal. |
| f. | Connect the battery negative (-) terminal. |
|
|
Electrical Specified Value Inspection (Using the Voltmeter and Clamp type Ammeter)
| 1. | Voltage Drop Test Of Alternator Output Wire This test determines whether or not the wiring between the alternator "B" terminal and the battery (+) terminal is good by the voltage drop method. | (1) | Preparation | a. | Turn the ignition switch to "OFF". |
| b. | Install the clamp type ammeter between battery positive (+) and alternator "B" terminal. |
| c. | Connect the (+) lead wire of voltmeter to the "B" terminal of alternator and the (-) lead wire of voltmeter to the (+) terminal of battery. |
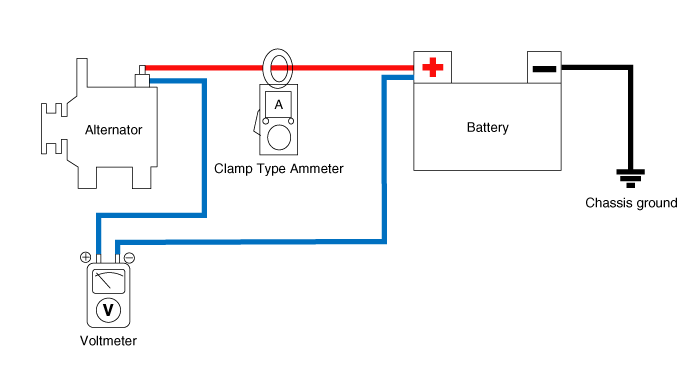
|
| (2) | Test | b. | Turn on the headlamps and blower motor, and set the engine speed until the ammeter indicates 20A.And then, read the voltmeter at this time. |
|
| (3) | Result | a. | The voltmeter may indicate the standard value. Standard value : 0.2V max |
|
| b. | If the value of the voltmeter is higher than expected (above 0.2V max.), poor wiring is suspected. In this case check the wiring from the alternator "B" terminal to the battery (+) terminal. Check for loose connections, color change due to an over-heated harness, etc. Correct them before testing again. |
| c. | Upon completion of the test, set the engine speed at idle.Turn off the headlamps, blower motor and the ignition switch. |
|
|
| 2. | Output Current Test This test determines whether or not the alternator gives an output current that is equivalent to the normal output. | (1) | Preparation | a. | Prior to the test, check the following items and correct as necessary. Check the battery installed in the vehicle to ensure that it is good condition. The battery checking method is described in the section "Battery". The battery that is used to test the output current should be one that has been partially discharged. With a fully charged battery, the test may not be conducted correctly due to an insufficient load. Check the tension of the alternator drive belt. The belt tension check method is described in the section "Inspect drive belt". |
| b. | Turn off the ignition switch. |
| c. | Disconnect the battery negative (-) terminal. |
| d. | Install the clamp type ammeter between battery positive (+) and alternator "B" terminal. |
| e. | Connect a DC ammeter (0 to 150A) in series between the "B" terminal and the disconnected output wire. Be sure to connect the (-) lead wire of the ammeter to the disconnected output wire. | •
| Tighten each connection securely, as a heavy current will flow. Do not rely on clips. |
|
|
| f. | Connect a voltmeter (0 to 20V) between the "B" terminal and ground. Connect the (+) lead wire to the alternator "B" terminal and (-) lead wire to a good ground. |
| g. | Connect the battery negative (-) terminal. |
| h. | Leave the engine hood open. 

|
|
| (2) | Test | a. | Check to see that the voltmeter reads as the same value as the battery voltage. If the voltmeter reads 0V, and the open circuit in the wire between alternator "B" terminal and battery (+) terminal or poor grounding is suspected. |
| b. | Start the engine and turn on the headlamps. |
| c. | Set the headlamps to high beam and the heater blower switch to HIGH, quickly increase the engine speed to 2,500 rpm and read the maximum output current value indicated by the ammeter. | •
| After the engine start up, the charging current quickly drops. Therefore, the above operation must be done quickly to read the maximum current value correctly. |
|
|
|
| (3) | Result | a. | The ammeter reading must be higher than the limit value. If it is lower but the alternator output wire is in good condition, remove the alternator from the vehicle and test it. Limit value : Rated current 60% |
| •
| The nominal output current value is shown on the nameplate affixed to the alternator body. |
|
| •
| The output current value changes with the electrical load and the temperature of the alternator itself.Therefore, the nominal output current may not be obtained. If such is the case, keep the headlamps on the cause discharge of the battery, or use the lights of another vehicle to increase the electrical load. The nominal output current may not be obtained if the temperature of the alternator itself or ambient temperature is too high. In such a case, reduce the temperature before testing again. |
|
|
| b. | Upon completion of the output current test, lower the engine speed to idle and turn off the ignition switch |
| c. | Disconnect the battery negative (-) terminal. |
| d. | Remove the ammeter and voltmeter and the engine tachometer. |
| e. | Connect the alternator output wire to the alternator "B" terminal. |
| f. | Connect the battery negative (-) terminal. |
|
|
| 3. | Regulated Voltage Test The purpose of this test is to check that the electronic voltage regulator controls voltage correctly. | (1) | Preparation | a. | Prior to the test, check the following items and correct if necessary. Check that the battery installed on the vehicle is fully charged. The battery checking method is described in the section "Battery". Check the alternator drive belt tension. The belt tension check method is described in the section "Inspect drive belt". |
| b. | Turn ignition switch to "OFF". |
| c. | Disconnect the battery negative (-) terminal. |
| d. | Connect a digital voltmeter between the "B" terminal of the alternator and ground. Connect the (+) lead of the voltmeter to the "B" terminal of the alternator. Connect the (-) lead to good ground or the battery (-) terminal. |
| e. | Disconnect the alternator output wire from the alternator "B" terminal. |
| f. | Connect a DC ammeter (0 to 150A) in series between the "B" terminal and the disconnected output wire. Connect the (-) lead wire of the ammeter to the disconnected output wire. |
| g. | Connect the battery negative (-) terminal. 

|
|
| (2) | Test | a. | Turn on the ignition switch and check to see that the voltmeter indicates the following value. Voltage : Battery voltage |
If it reads 0V, there is an open circuit in the wire between the alternator "B" terminal and the battery and the battery (-) terminal. |
| b. | Start the engine. Keep all lights and accessories off. |
| c. | Run the engine at a speed of about 2,500 rpm and read the voltmeter when the alternator output current drops to 10A or less |
|
| (3) | Result | a. | If the voltmeter reading dosen't agree with the standard value, the voltage regulator or the alternator is faulty. Regulated Voltage : 11.7 - 15.3V |
|
| b. | If the voltmeter reading dosen't agree with the standard value, the voltage regulator or the alternator is faulty. |
| c. | Disconnect the battery negative (-) terminal. |
| d. | Remove the voltmeter and ammeter. |
| e. | Connect the alternator output wire to the alternator "B" terminal. |
| f. | Connect the battery negative (-) terminal. |
|
|
Vehicle parasitic current inspection
[Using the Ammeter]
| 1. | Turn the all electric devices OFF, and then turn the ignition switch OFF. |
| 2. | Close all doors except the engine hood, and then lock all doors. | (1) | Disconnect the hood switch connector. |
| (3) | Close the doors or remove the door switches. |
|
| 3. | Wait a few minutes until the vehicle’s electrical systems go to sleep mode. | •
| For an accurate measurement of a vehicle parasitic current, all electrical systems should go to sleep mode. (It takes at least one hour or at most one day.) However, an approximate vehicle parasitic current can be measured after 10-20 minutes. |
|
|
| 4. | Connect an ammeter in series between the battery (-) terminal and the ground cable, and then disconnect the clamp from the battery (-) terminal slowly. | •
| Be careful that the lead wires of an ammeter do not come off from the battery (-) terminal and the ground cable to prevent the battery from being reset. In case the battery is reset, connect the battery cable again, and then start the engine or turn the ignition switch ON for more than 10 sec. Repeat the procedure from No. 1. To prevent the battery from being reset during the inspection, |
| 1) | Connect a jump cable between the battery (-) terminal and the ground cable. |
| 2) | Disconnect the ground cable from the battery (-) terminal. |
| 3) | Connect an ammeter between the battery (-) terminal and the ground cable. |
| 4) | After disconnecting the jump cable, read the current value of the ammeter. |
|
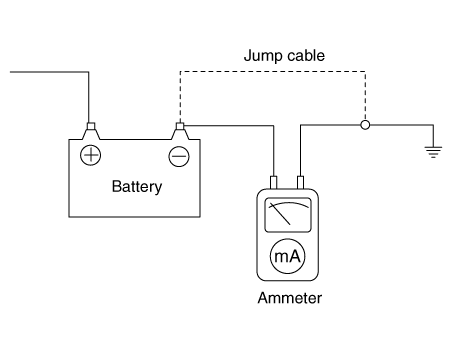
|
| 5. | Read the current value of the ammeter. | •
| If the parasitic current is over the limit value, search for abnormal circuit by removing a fuse one by one and checking the parasitic current. |
| •
| Reconnect the suspected parasitic currentdraw circuit fuse only and search for suspectedunit by removing the component connected with thecircuit one by one until the parasitic draw dropsbelow limit value. |
Limit value (after 10 - 20 min.) : Below 50 mA |
|
[Using the Clamp type Ammeter]
| 6. | Turn the all electric devices OFF, and then turn the ignition switch OFF. |
| 7. | Close all doors except the engine hood, and then lock all doors. | (1) | Disconnect the hood switch connector. |
| (3) | Close the doors or remove the door switches. |
|
| 8. | Wait a few minutes until the vehicle’s electrical systems go to sleep mode. | •
| For an accurate measurement of a vehicle parasitic current, all electrical systems should go to sleep mode. (It takes at least one hour or at most one day.) However, an approximate vehicle parasitic current can be measured after 10-20 minutes. |
|
|
| 9. | Install the clamp type ammerter on battery negative (-) terminal. 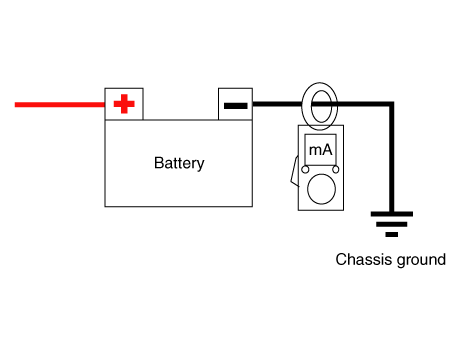
|
| 10. | Read the current value of the ammeter. | •
| If the parasitic current is over the limit value, search for abnormal circuit by removing a fuse one by one and checking the parasitic current. |
| •
| Reconnect the suspected parasitic currentdraw circuit fuse only and search for suspectedunit by removing the component connected with thecircuit one by one until the parasitic draw dropsbelow limit value. |
Limit value (after 10 - 20 min.) : Below 50 mA |
|
Alternator
Description and operation
The Alternator has eight built-in diodes, each rectifying AC current to DC current.
Therefore, DC current appears at alternator "B" terminal.
In addition, the charging voltage of this alternator is regulated by the battery voltage detection system.
The alternator is regulated by the battery voltage detection system.
The main components of the alternator are the rotor, stator, rectifier, capacitor brushes, bearings and V-ribbed belt pulley.
The brush holder contains a built-in electronic voltage regulator.
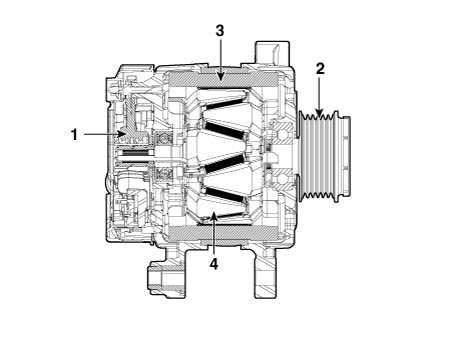
1. Brush
2. Drive belt pully
3. Stator
4. Rotor
|
Specifications
Item
|
Specification
|
Rated voltage
| 13.5V, 130A
|
Speed in use
| 1,000 - 18,000 rpm
|
Voltage regulator
| IC Regulator built-in type
|
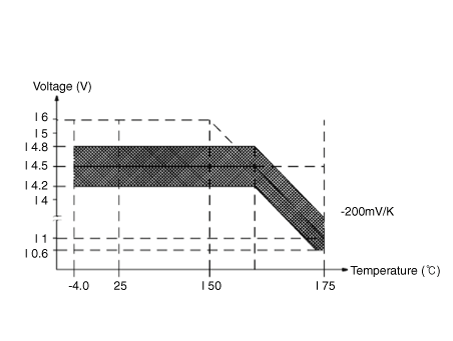
Regulator Setting Voltage
| External mode
| 10.6 - 16 ± 0.3V
|
Internal mode
| 14.55 ± 0.3V
|
Temperature Gradient
| External mode
| 0 ± 2 mV / °C
|
Internal mode
| -3.5 ± 2mV / °C
|
Schematic diagrams
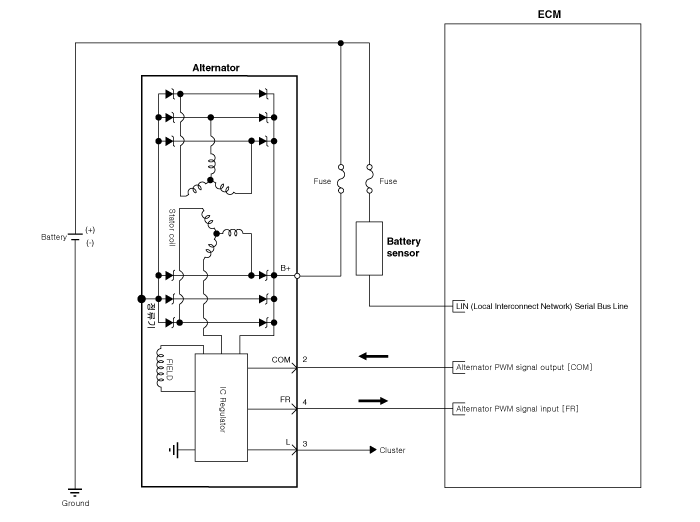
| •
|
COM signal - When controlling the voltage generated, the ECM sends the target voltage data to the alternator via a PWM signal. (High Voltage : 4V, Low Voltage : 2V) |
| •
|
FR signal - The transistor activation signal inside the alternator monitors the voltage generated by the alternator to control the excitation current before it sends the FR signal to the ECM. (At certain RPM/electric loads, the FR duty can remain static. However, more often, the RPM, electric load, target voltage, etc. are always changing in the vehicle, so the FR must also change constantly) |
| •
|
L signal - Turns on the battery warning lamp on the dashboard when the battery charging system malfunctions. (Conditions for turning on the lamp - overcharge, over discharge, a field coil blown inside the alternator) |
| •
|
B+ terminal - The output voltage from the generator travels to the battery via the B+ terminal. |
|
Repair procedures
| 1. | Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect the negative (-) battery cable. |
| 2. | Remove the drive belt tensioner. (Refer to Engine Mechanical System - "Drive Belt Tensioner") |
| 3. | Remove the drive belt. (Refer to Engine Mechanical System - "Drive Belt") |
| 4. | Remove return hose & pipe braket bolt (A). Tightening torque : 9.8 - 11.8 N.m (1.0 - 1.2 kgf.m, 7.2 - 8.7 lb-ft) |
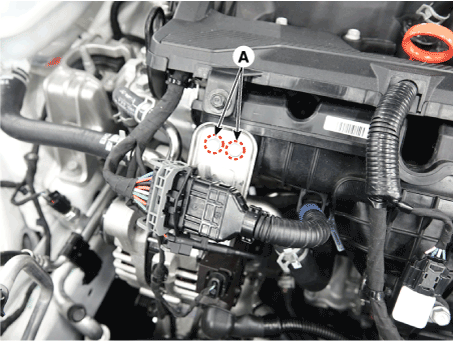
|
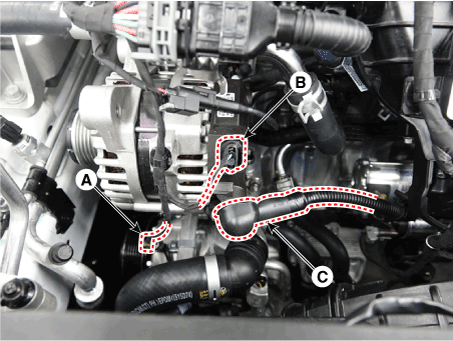
| 5. | Disconnect the cable (C) from alternator "B" terminal after disconnect the compressor connector (A) and the alternator connector (B). Tightening torque : 9.8 - 11.8 N.m (1.0 - 1.2 kgf.m, 7.2 - 8.7 lb-ft) |
|
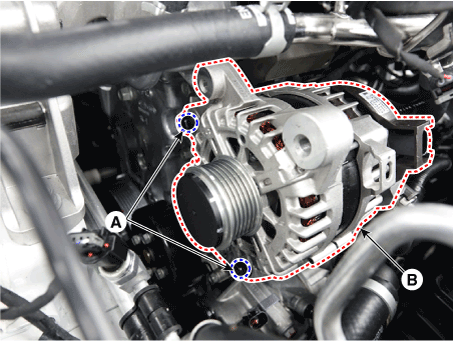
| 6. | Remove the alternator (B) after loosening the mounting nuts (A). Tightening torque : 40.03 - 63.7 N.m (5.0 - 6.5 kgf.m, 36.1 - 47.0 lb-ft) |
|
| 1. | Install in the reverse order of removal. |
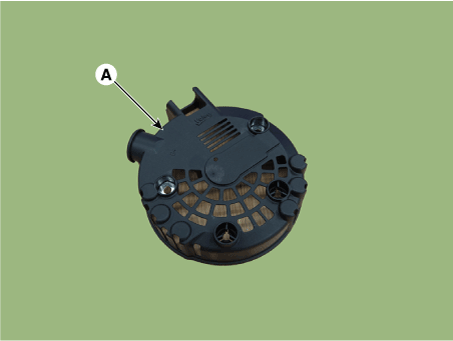
| 1. | Remove the rear cover (A). 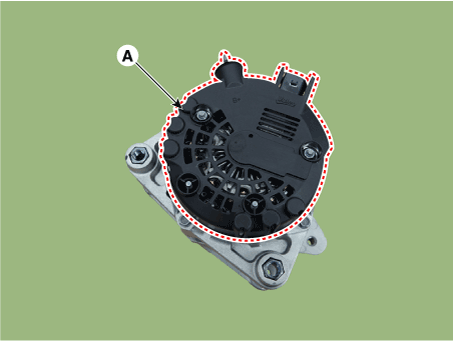
|
| 2. | Remove the mounting bolts and the regulator assembly (A). | •
| When removing take care not to damage the surrounding parts. 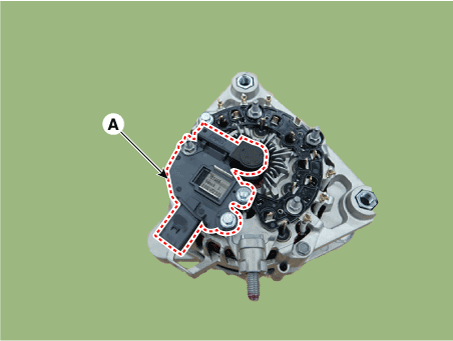
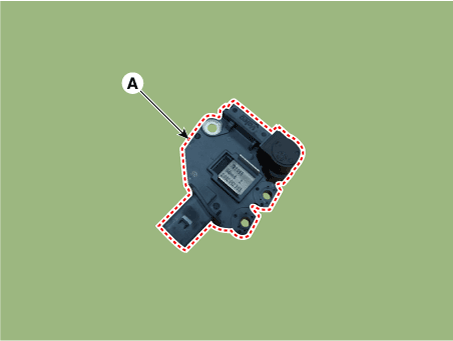
|
|
|
| 3. | Remove the OAP cap (A). 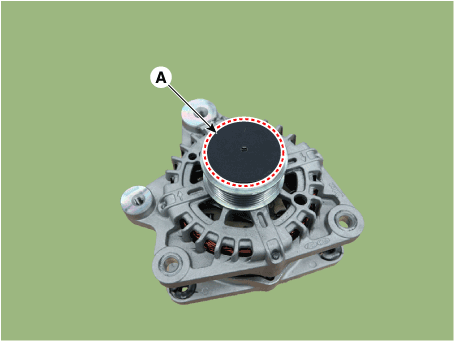
| •
| When installing, replace with new OAP cap. |
|
|
| 4. | Remove the OAP pulley (A) by using the SST (09373-27000). 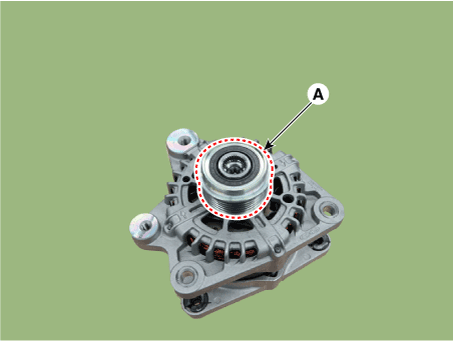
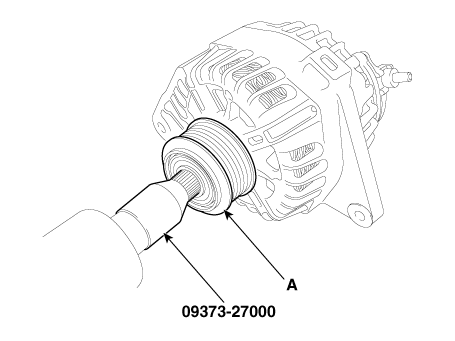
|
| 5. | Remove the rectifier assembly (A) after disconnecting the stator leads. 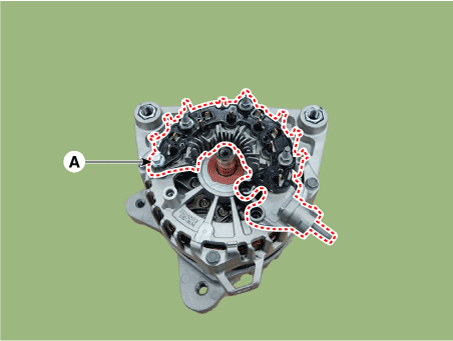
|
| 6. | Remove the through bolts (A). 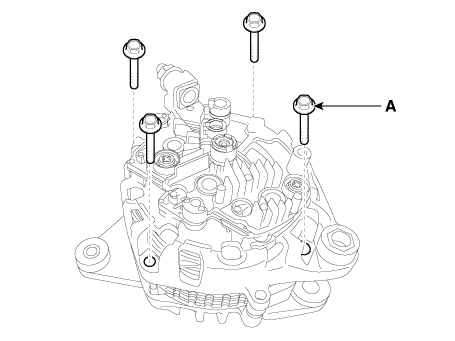
|
| 7. | Disconnect the rotor (A) and housing (B). 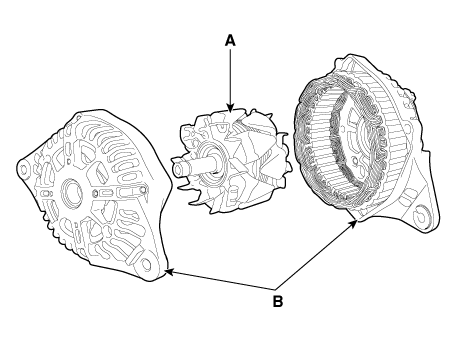
|
| 1. | Reassemble in the reverse order of disassembly. |
[Rotor]
| 1. | Check that there is continuity between the slip rings (C). 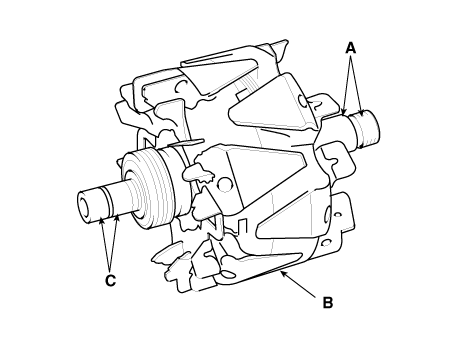
|
| 2. | Check that there is no continuity between the slip ring (C) and the rotor (B) or rotor shaft (A). |
| 3. | If the rotor fails either continuity check, replace the alternator. |
[Stator]
| 1. | Check that there is continuity between each pair of leads (A). 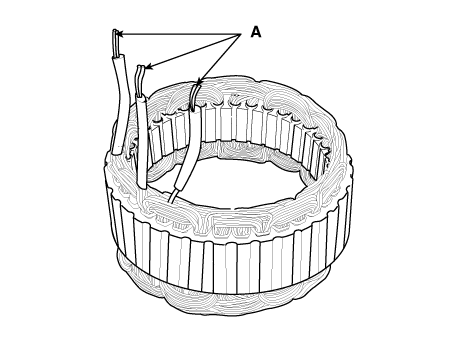
|
| 2. | Check that there is no continuity between each lead and the coil core. |
| 3. | If the coil fails either continuity check, replace the alternator. |
Battery
Description and operation
| 1. | The CMF (Closed Maintenance Free) battery is, as the name implies, totally maintenance free and has no removable battery cell caps. |
| 2. | The MF (Closed Maintenance Free) battery does not require water replenishment for the repair. |
| 3. | The battery is completely sealed, except for small vent holes in the cover. 
| •
| After disconnecting then reconnecting the battery negative cable, reset some parts that require the reset procedures. (Refer to Body Electrical System – "General Information") |
|
|
Specifications
▶CMF68L-DIN
Item
|
Specification
|
Model typeModel type
| CMF68L-DIN
|
Capacity [20HR/5HR] (AH)
| 68 / 54
|
Cold Cranking Amperage (A)
| 760 (SAE / EN)
|
Reserve Capacity (Min)
| 110
|
| •
| Model type description 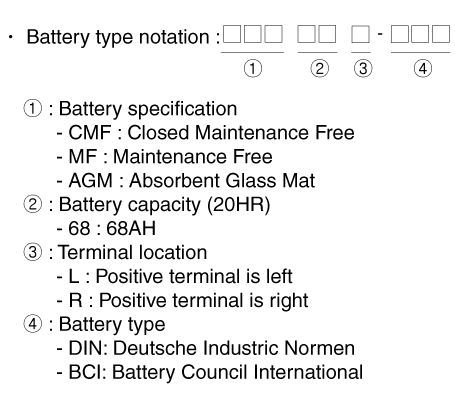
|
| •
| Cold Cranking Ampere (CCA) : Cold Cranking Amps is a rating used in the battery industry to define a battery's ability to start an engine in cold temperatures. |
| –
| The rating is the number of amps a new, fully charged battery can deliver at -18°C (-0.4°F) for 30 seconds, while maintaining a voltage of at least 7.2 volts for a 12 volt battery. |
| –
| The higher the CCA rating, the greater the starting power of the battery. |
| •
| RESERVE CAPACITY (RC) : Reserve Capacity is a battery industry rating, defining a battery's ability to power a vehicle with an inoperative alternator or fan belt. |
| –
| The rating is the number of minutes a battery at 26.7°C (80°F) can be discharged at 25 amps and maintain a voltage of 10.5 volts for a 12 volt battery. |
| –
| The higher the reserve rating, the longer your vehicle can operate should your alternator or fan belt fail. |
|
Troubleshooting
Repair procedures
Battery
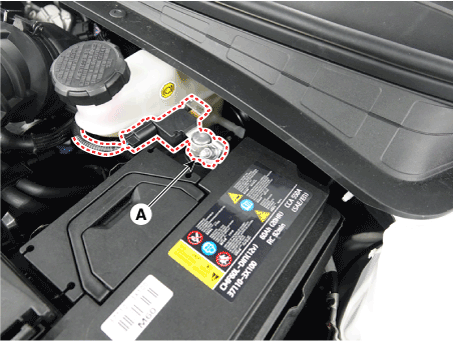
| 1. | Turn the ignition switch OFF. |
| 2. | Disconnect the battery (-) terminal (A). Battery (-)terminal installation : 4.0 - 6.0 N.m (0.4 - 0.6 kgf.m, 3.0 - 4.4 lb-ft) |
|
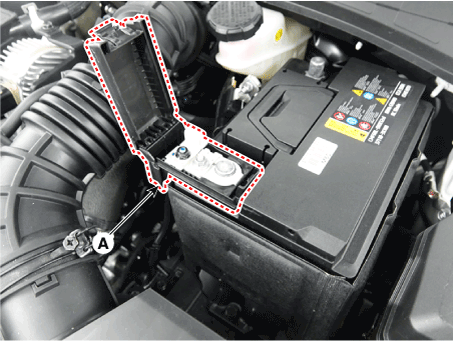
| 3. | Remove the battery (+) terminal (A). Battery (+) terminal installation : 7.8 - 9.8 N.m (0.8 - 1.0 kgf.m, 5.8 - 7.2 lb-ft) |
|
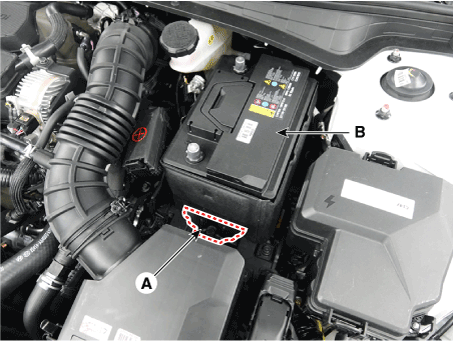
| 4. | Remove the battery mouting bracket (A). |
| 5. | Remove the battery insulation pad after removing the battery (B). Battery mounting bracket installation bolt : 19.6 - 29.4 N.m (1.9 - 3.0 kgf.m, 13.7 - 30.4 Ib-ft) |
|
Battery tray
| 1. | Remove the battery. (Refer to "Removal") |
| 2. | Remove the air cleaner assembly. (Refer to Engine Mechanical System - "Air Cleaner") |
| 3. | Remove the ECM. (Refer to Engine Control / Fuel System - "Engine Control Module (ECM)") |
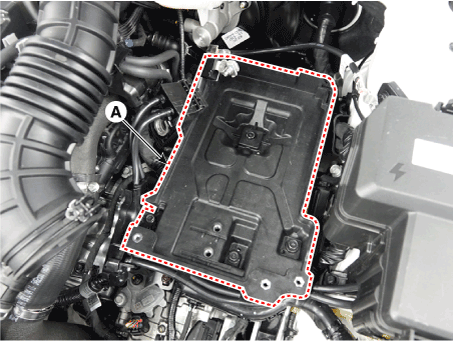
| 4. | Remove the battery tray (A) after loosening the bolts. Battery tray installation bolt : 19.6 - 29.4 N.m (1.9 - 3.0 kgf.m, 13.7 - 30.4 Ib-ft) |
|
| 1. | Install in the reverse order of removal. | •
| When installing the battery, fix the mounting bracket on the tray correctly. |
|
|
Vehicle Parasitic current inspection
| 1. | Turn the all electric devices OFF, and then turn the ignition switch OFF. |
| 2. | Close all doors except the engine hood, and then lock all doors. | (1) | Disconnect the hood switch connector. |
| (3) | Close the doors or remove the door switches. |
|
| 3. | Wait a few minutes until the vehicle’s electrical systems go to sleep mode. | •
| For an accurate measurement of a vehicle parasitic current, all electriacl systems should go to sleep mode. (It takes at least one hour or at most one day.) However, an approximate vehicle parasitic current can be measured after 10-20 minutes. |
|
|
| 4. | Connect an ammeter in series between the battery (-) terminal and the ground cable, and then disconnect the clamp from the battery (-) terminal slowly. | •
| Be careful that the lead wires of an ammeter do not come off from the battery (-) terminal and the ground cable to prevent the battery from being reset. In case the battery is reset, connect the battery cable again, and then start the engine or turn the ignition switch ON for more than 10 sec. Repeat the procedure from No. 1. |
| a. | Connect a jump cable between the battery (-) terminal and the ground cable. |
| b. | Disconnect the ground cable from the battery (-) terminal. |
| c. | Connect an ammeter between the battery (-) terminal and the ground cable. |
| d. | After disconnecting the jump cable, read the current value of the ammeter. |
|
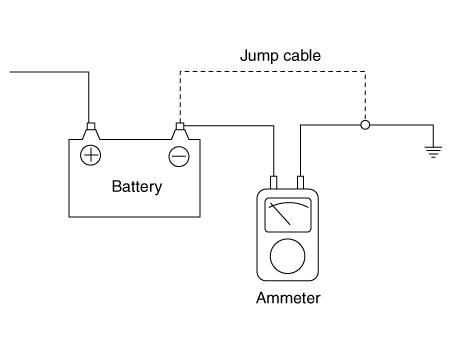
|
| 5. | Read the current value of the ammeter. | •
| If the parasitic current is over the limit value, search for abnormal circuit by removing a fuse one by one and checking the parasitic current. |
| •
| Reconnect the suspected parasitic current draw circuit fuse only and search for suspected unit by removing a compoconnected with the circuit one by one until the parasitic draw drops below limit value. |
Limit value (after 10 - 20 min.) : Below 50 mA |
|
| 1. | Make sure the ignition switch and all accessories are in the OFF position. |
| 2. | Disconnect the battery negative cables (A). |
| 3. | Remove the battery from the vehicle. (Refer to Charging System - "Battery") | •
| Care should be taken in the event the battery case is cracked or leaking, to protect your skin from the electrolyte. |
| •
| Heavy rubber gloves (not the household type) should be worn when removing the battery. 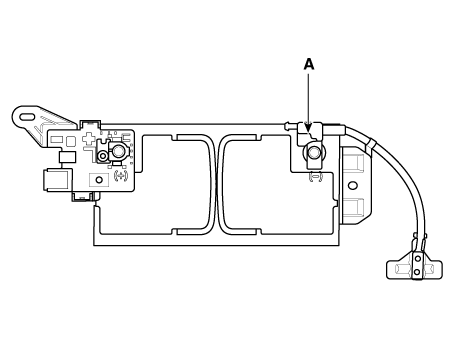
|
|
|
| 4. | Inspect the battery tray for damage caused by the loss of electrolyte. If acid damage is present, it will be necessary to clean the area with a solution of clean warm water and baking soda. Scrub the area with a stiff brush and wipe off with a cloth moistened with baking soda and water. |
| 5. | Clean the top of the battery with the same solution as described above. |
| 6. | Inspect the battery case and cover for cracks. If cracks are present, the battery must be replaced. |
| 7. | Clean the battery posts with a suitable battery post tool. |
| 8. | Clean the inside surface of the terminal clamps with a suitable battery cleaning tool. Replace damaged or frayed cables and broken terminal clamps. |
| 9. | Install the battery in the vehicle. |
| 10. | Connect the cable terminals to the battery post, making sure tops of the terminals are flush with the tops of the posts. |
| 11. | Tighten the terminal nuts securely. |
| 12. | Coat all connections with light mineral grease after tightening. | •
| When batteries are being charged, an explosive gas forms beneath the cover of each cell. Do not smoke near batteries being charged or which have recently been charged. Do not break live circuit at the terminals of batteries being charged. |
| •
| A spark will occur when the circuit is broken. Keep open flames away from battery. 
|
|
|
Battery Sensor
Description and operation
Vehicles have many control units that use more electricity. These units control their own system based on information from diverse sensors. It is important to have a stable power supply as there diverse sensors giving a variety of information. Battery sensor is mounted on battery (-) terminal. It transmits battery voltage, current, temperature information to ECM. ECM controls generating voltage by duty cycle based on these signals.
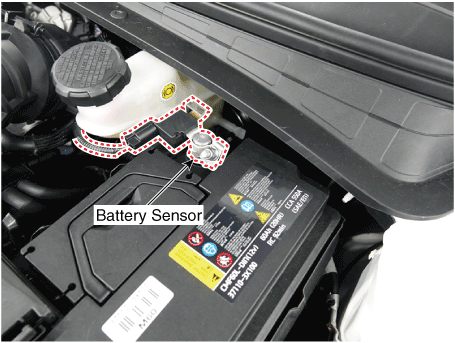
Repair procedures
| 1. | Turn the ignition switch OFF. |
| 2. | Disconnect the battery (-) terminal (A). Battery (-)terminal installation : 4.0 - 6.0 N.m (0.4 - 0.6 kgf.m, 3.0 - 4.4 lb-ft) |

|
| 3. | Remove the battery. (Refer to Engine Electrical System - "Battery") |
| 4. | Remove the battery negative (-) cable after removing the bolts (A). Battery sensor cable installation bolt : 10.8 - 13.7 N.m (1.1 - 1.4 kgf.m, 8.0 -10.1 lb-ft) |
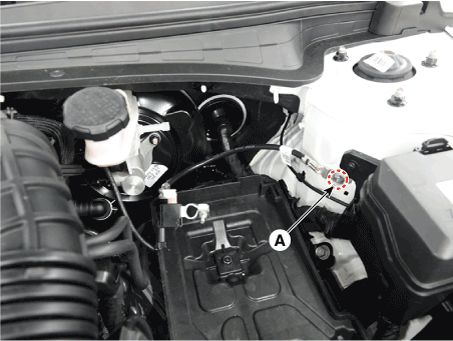
|
| 1. | Install in the reverse order of removal. |
Description and operation
DescriptionIgnition timing is controlled by the electronic control ignition timing system. The standard reference ignition timing data for the engine operating conditions ...
Description and operation
DescriptionThe starting system includes the battery, starter, solenoid switch, ignition switch, inhibitor switch (A/T), clutch pedal switch (M/T), ignition lock switch, co ...
 Hyundai Elantra CN7: Charging System
Hyundai Elantra CN7: Charging System